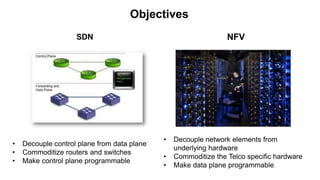
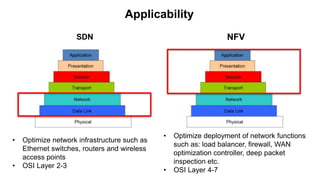
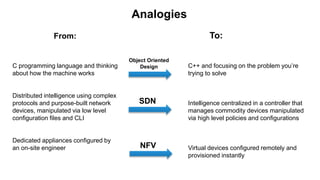
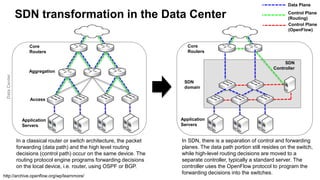
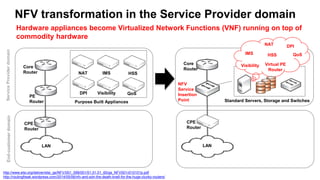
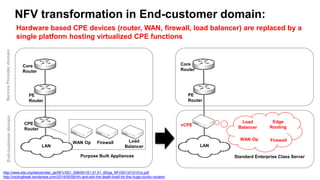
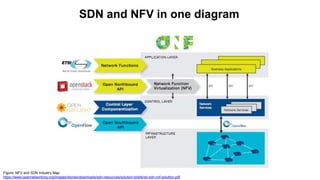
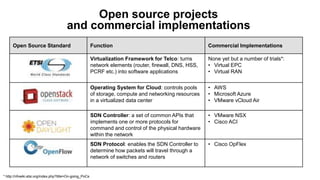
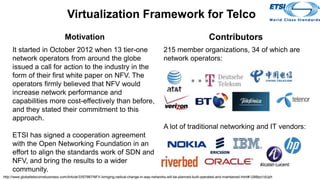
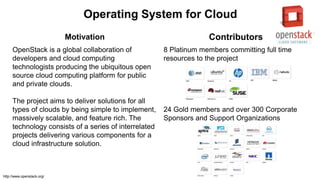
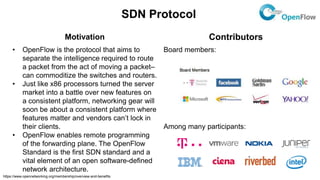
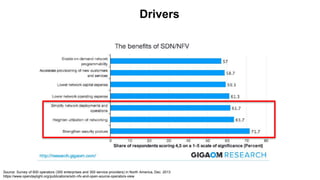
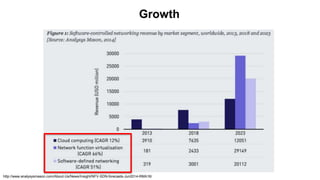
The document discusses the relationship between Software-Defined Networking (SDN) and Network Functions Virtualization (NFV), highlighting their objectives to decouple the control and data planes, optimize network infrastructure, and improve operational efficiency. It outlines the benefits of adopting SDN and NFV, such as reduced costs, increased agility, and simplified configurations, while also noting industry standards and transformations in data centers and service providers. Additionally, it mentions key open-source projects and collaborations aimed at enhancing the functionality and implementation of these technologies.