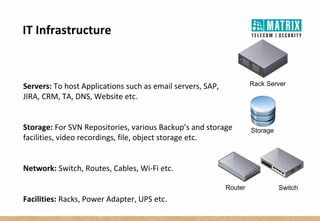
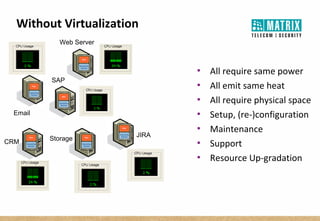
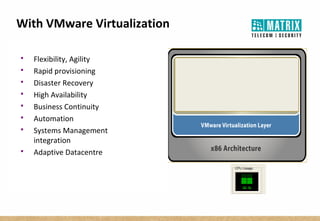
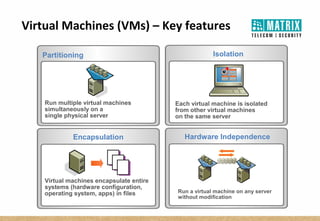
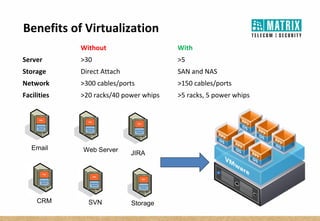
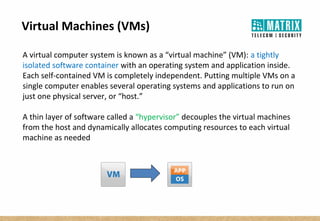
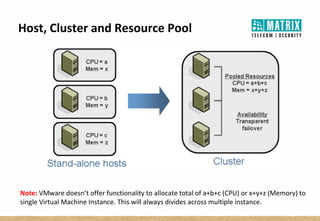
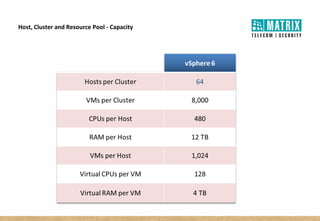
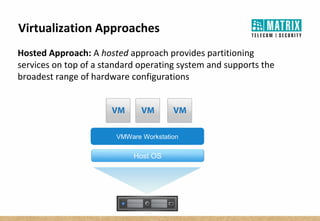
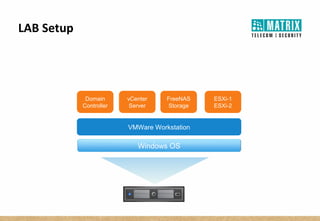
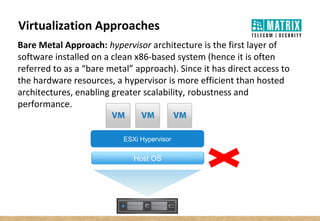
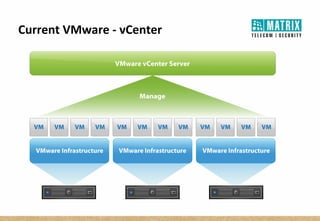
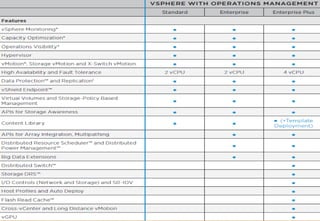
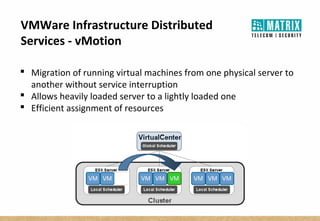
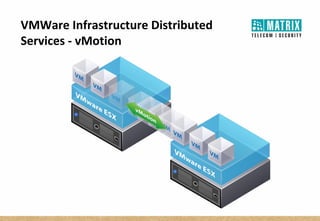
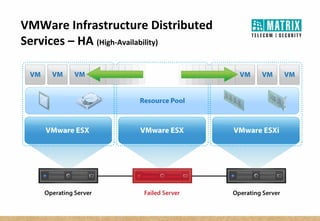
Virtualization allows multiple virtual machines to run on a single physical server, improving flexibility, efficiency, and reducing costs. It enables benefits like rapid provisioning, disaster recovery, high availability, and easier systems management by encapsulating entire systems as files that can run independently on any server. Virtual machines are isolated software containers that have independent operating systems and applications. A hypervisor manages resource allocation to virtual machines dynamically based on their needs.