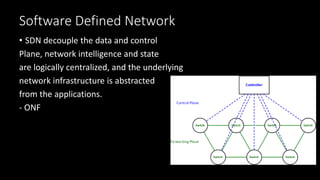
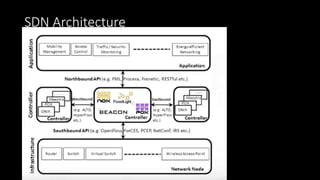
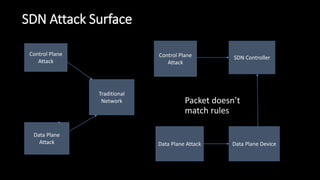
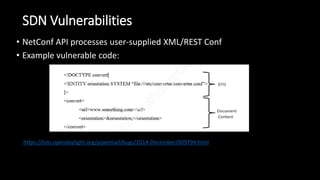
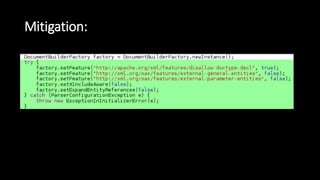
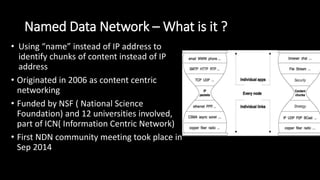
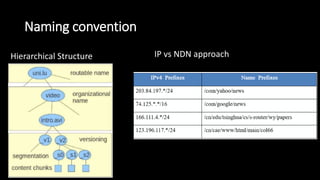
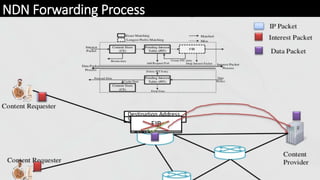
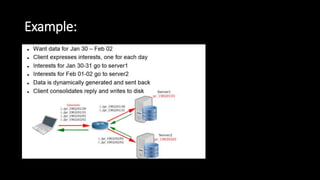
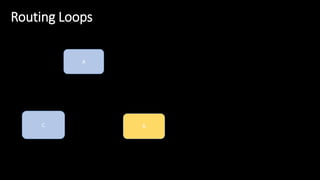
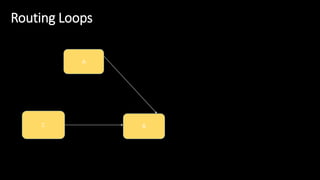
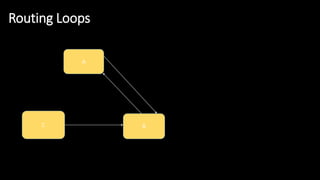
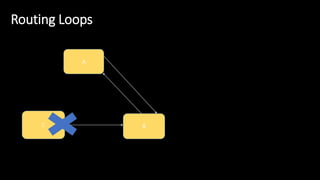
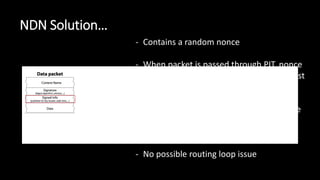
The document discusses the security implications of Software Defined Networking (SDN) and Named Data Networking (NDN), highlighting their architectures, advantages, vulnerabilities, and mitigation strategies. It addresses the centralized management and dynamic nature of SDN, while emphasizing NDN's content-centric approach and its benefits in security and routing. The conclusion suggests a paradigm shift towards securing content rather than just the communication channels.