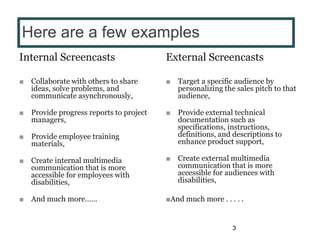
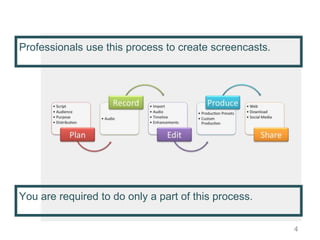
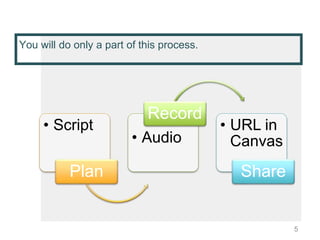
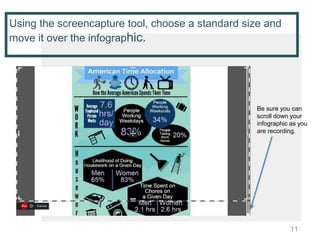
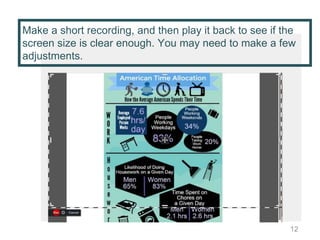
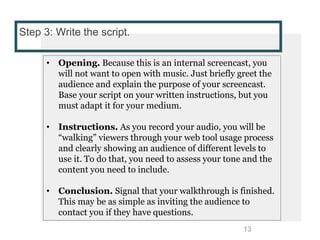
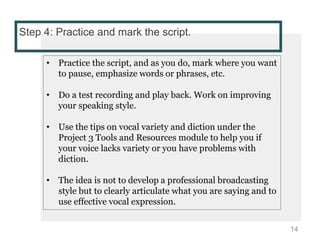
This document provides instructions for creating screencasts. It discusses what screencasts are, which are video recordings of computer screen output that often include audio narration. It outlines different uses of screencasts, such as for employee training, project updates, and external technical documentation. The document then gives a 5-step process for creating a screencast: choosing a screencasting tool, selecting the screen size, writing a script, practicing the script, and recording the screencast. It provides guidance for each step, such as recommending free tools like Screencastomatic or Jing, tips for choosing an appropriate screen size, elements to include in the script, best practices for practicing and marking up the script,