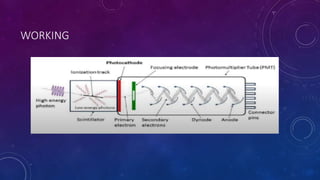
A scintillation counter is an instrument used to detect and measure ionizing radiation by utilizing the excitation effect of radiation on scintillating materials, producing light impulses proportional to the energy of the radiation. It operates using different classes of phosphors and photomultiplier tubes to enhance detection, with applications in medical imaging, environmental monitoring, nuclear security, and safety. Various materials like cesium iodide and sodium iodide serve as scintillators for detecting different types of radiation.