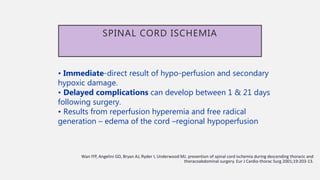
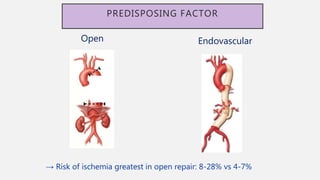
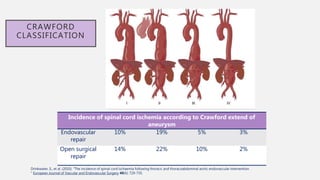
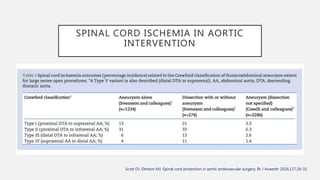
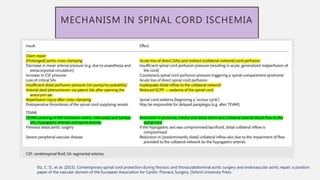
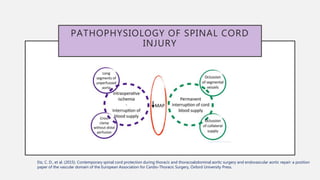
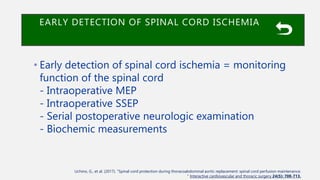
The document discusses spinal cord ischemia that can occur during aortic interventions. It outlines the anatomy of the spinal cord blood supply, which involves a network of arteries. Risk factors for spinal cord ischemia include longer aneurysm extent, hypotension, emergency operations, and open repair procedures. The pathophysiology involves impairment of autoregulation and reduction of spinal cord perfusion pressure during aortic occlusion from cross-clamping. Prevention strategies aim to minimize ischemia time, increase tolerance, augment spinal cord perfusion, and allow early detection of ischemia.





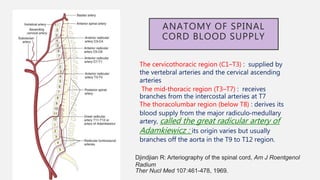
![ANATOMY OF SPINAL CORD BLOOD SUPPLY
The spinal cord receives blood from
spinal arteries derived from branches of
larger arteries
These major arteries include the
following:
• Vertebral arteries: arising from the
subclavian arteries in the neck.
• Ascending cervical arteries: arising
from a branch of the subclavian arteries.
• Posterior intercostal arteries: arising
from the thoracic aorta.
• Lumbar arteries: arising from the
abdominal aorta.
• Lateral sacral arteries: arising from
pelvic internal iliac arteries.
Gustavo S.(2017). Endovascular Aortic Repair [electronic resource] : Current Techniques with
Fenestrated, Branched and Parallel Stent-Grafts. Chapter 47](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sci-181030133005/85/Sci-6-320.jpg)
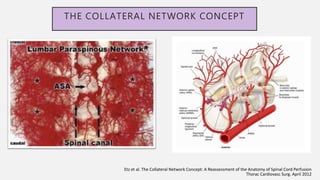
![ARTERY OF ADAMKIEWICZ
• Watershed region- Thoraco
lumbar segment.
Blood supply derived from large
radicular arteries called
ARM (Artery of Adamkiewicz)
Origin
T9-T12 – in 75%
T8-L3 – in 15%
L1-L2 – in 10% of patients.
Gustavo S.(2017). Endovascular Aortic Repair [electronic resource] : Current Techniques with
Fenestrated, Branched and Parallel Stent-Grafts. Chapter 47](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sci-181030133005/85/Sci-8-320.jpg)
![SPINAL CORD
ISCHEMIA
Gustavo S.(2017). Endovascular Aortic Repair [electronic resource] : Current Techniques with
Fenestrated, Branched and Parallel Stent-Grafts. Chapter 47](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sci-181030133005/85/Sci-10-320.jpg)


![TEVAR
- Large profile femoral
sheath
- The use of femoral
conduits For sheath
access
Gustavo S.(2017). Endovascular Aortic Repair [electronic resource] : Current Techniques with
Fenestrated, Branched and Parallel Stent-Grafts. Chapter 47](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sci-181030133005/85/Sci-22-320.jpg)
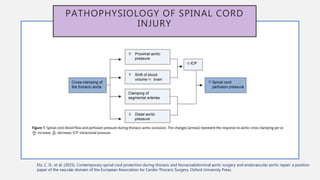
![SPINAL BLOOD FLOW AFTER THORACIC AORTIC
OCCLUSION (AORTIC CROSS CLAMPING)
Spinal cord perfusion pressure (SCPP )=
MABP – CSF pressure
> 50 – 60 mmHg to protect spinal cord
from ischemia
Normal CSF pressure = 13 – 15 mmHg
Temporary aortic cross-clamping decreases
SCBF and distal organ perfusion
Distal hypotension
Proximal hypertension
Increase in left ventricle afterload
Gustavo S.(2017). Endovascular Aortic Repair [electronic resource] : Current Techniques with Fenestrated, Branched and Parallel Stent-Grafts. Chapter 47](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sci-181030133005/85/Sci-26-320.jpg)

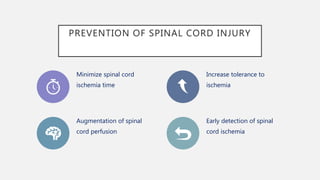

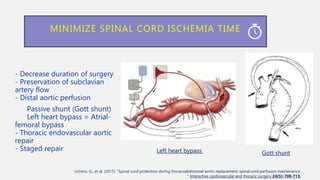




![INCREASE TOLERANCE TO ISCHEMIA
Gustavo S.(2017). Endovascular Aortic Repair [electronic resource] : Current Techniques with Fenestrated, Branched and Parallel Stent-Grafts. Chapter 47](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sci-181030133005/85/Sci-36-320.jpg)
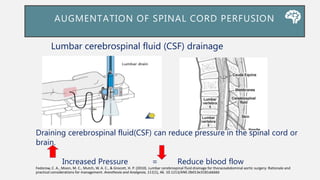
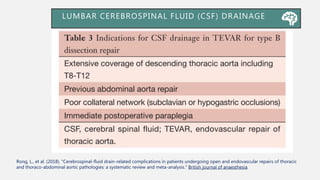
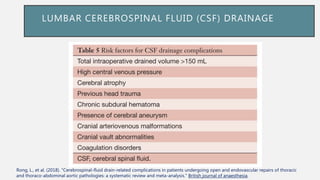
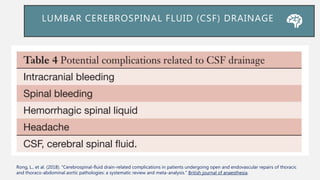
![LUMBAR CEREBROSPINAL FLUID (CSF)
DRAINAGE
Gustavo S.(2017). Endovascular Aortic Repair [electronic resource] : Current Techniques with
Fenestrated, Branched and Parallel Stent-Grafts. Chapter 47](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sci-181030133005/85/Sci-38-320.jpg)

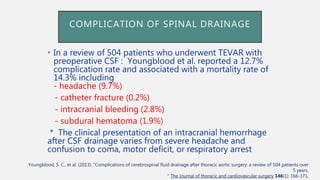
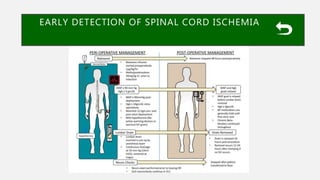
![SPINAL CORD ISCHEMIA AFTER AORTIC
SURGERY
• Overall 30-day and 36-month survivals in those
developing SCI were 92 % and 45%, respectively.
• In those patients that did not have resolution of their
symptoms, 3-month survival was reduced from 92 to
36 %.
• This highlights the devastating long-term outcomes of
patients suffering from profound SCI with paraplegia
Gustavo S.(2017). Endovascular Aortic Repair [electronic resource] : Current Techniques with
Fenestrated, Branched and Parallel Stent-Grafts. Chapter 47](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sci-181030133005/85/Sci-48-320.jpg)

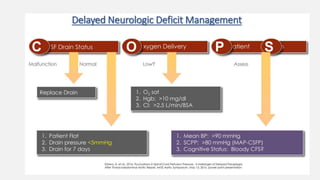
![BENEFIT OF CSF DRAINAGE
• CSF drainage is the only method aimed at mitigating SCI during
TAAA/DTA repair supported by randomised evidence.
• Class IB indication in the US guidelines
• Strong recommendation in high-risk patients in the European
guidelines.
• Spinal perfusion pressure = MAP - CSF pressure : a reduction in
CSF pressure should increasespinal blood flow
Gustavo S.(2017). Endovascular Aortic Repair [electronic resource] : Current Techniques with
Fenestrated, Branched and Parallel Stent-Grafts. Chapter 47](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sci-181030133005/85/Sci-50-320.jpg)
