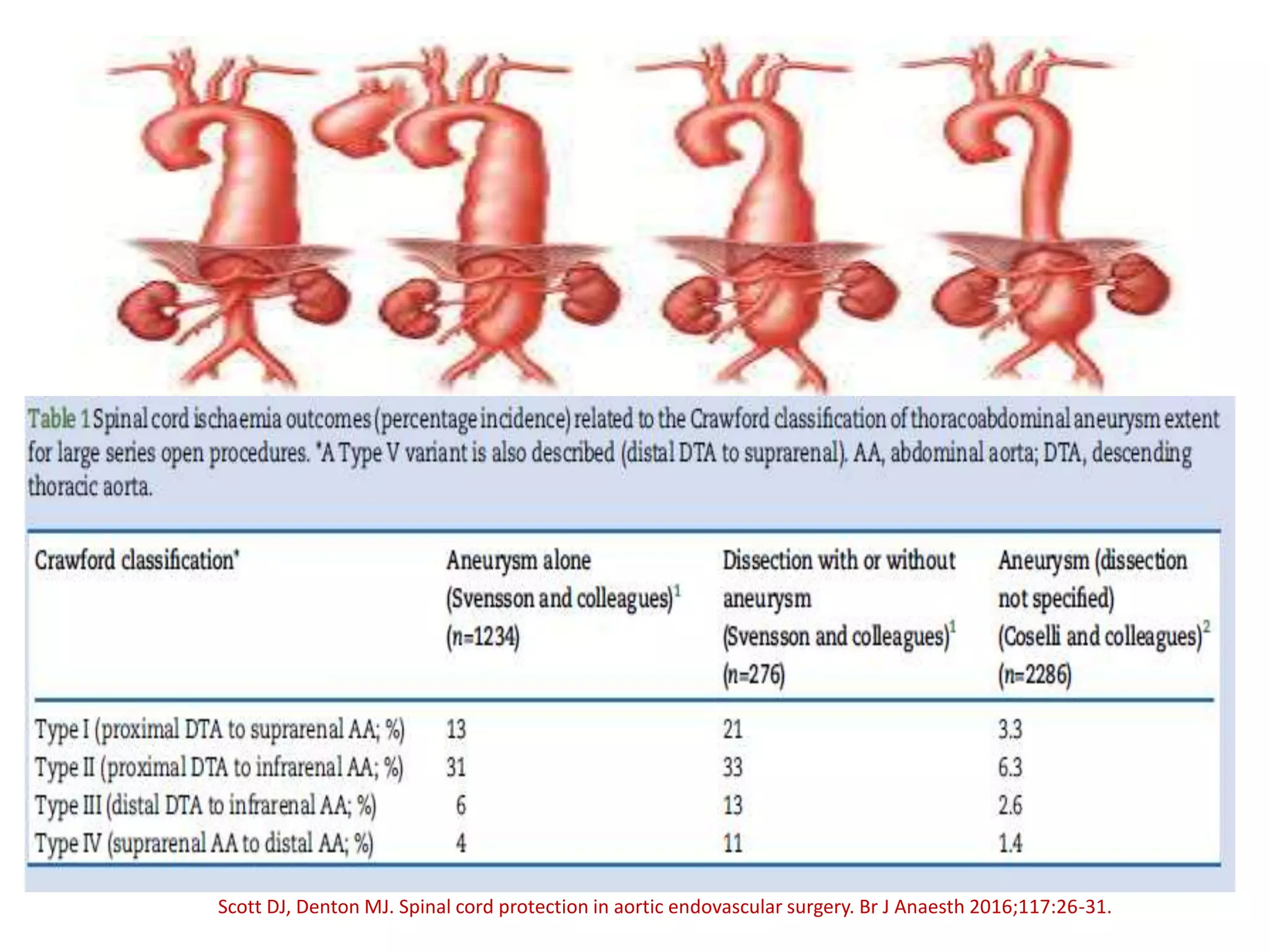
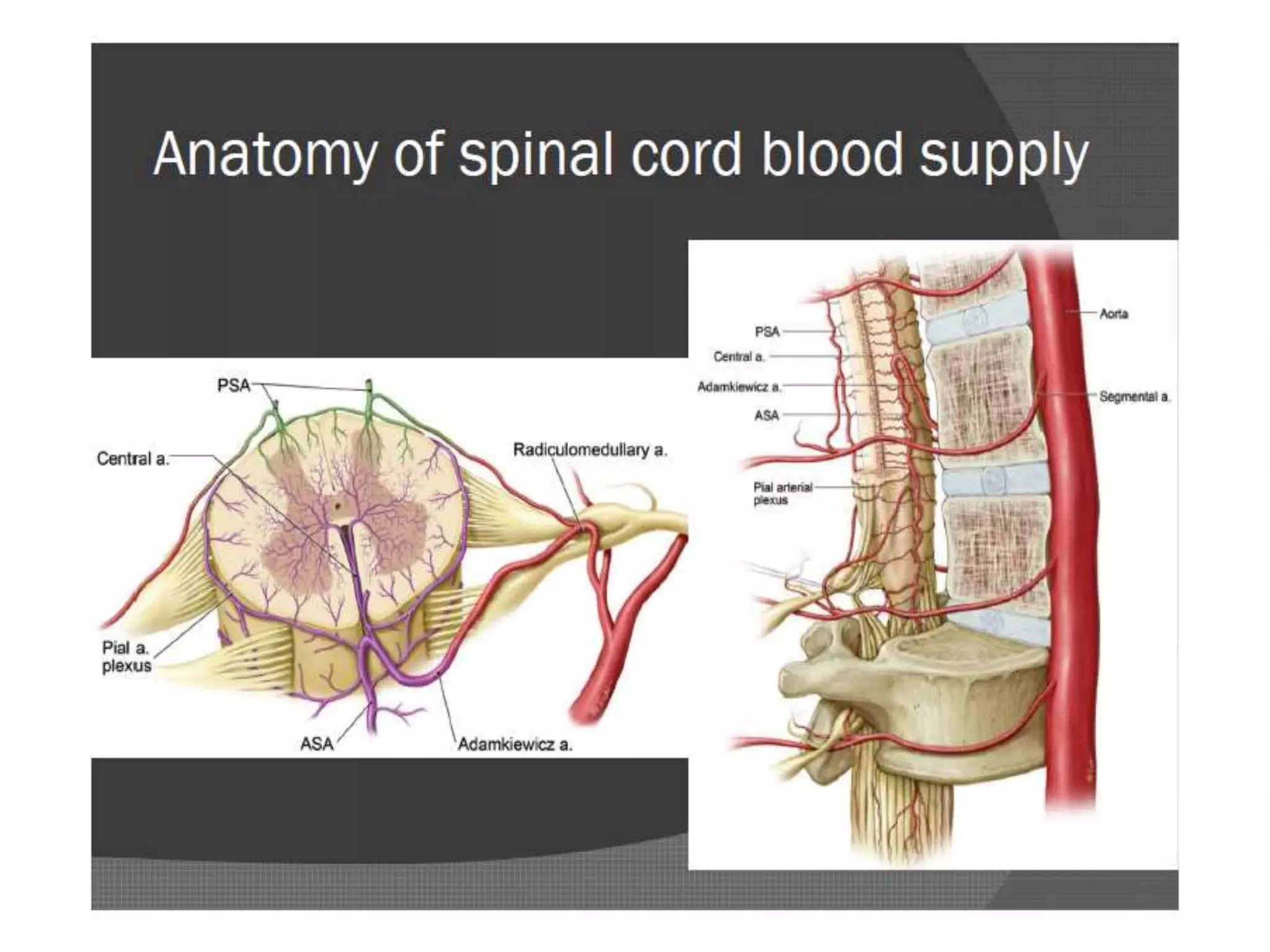
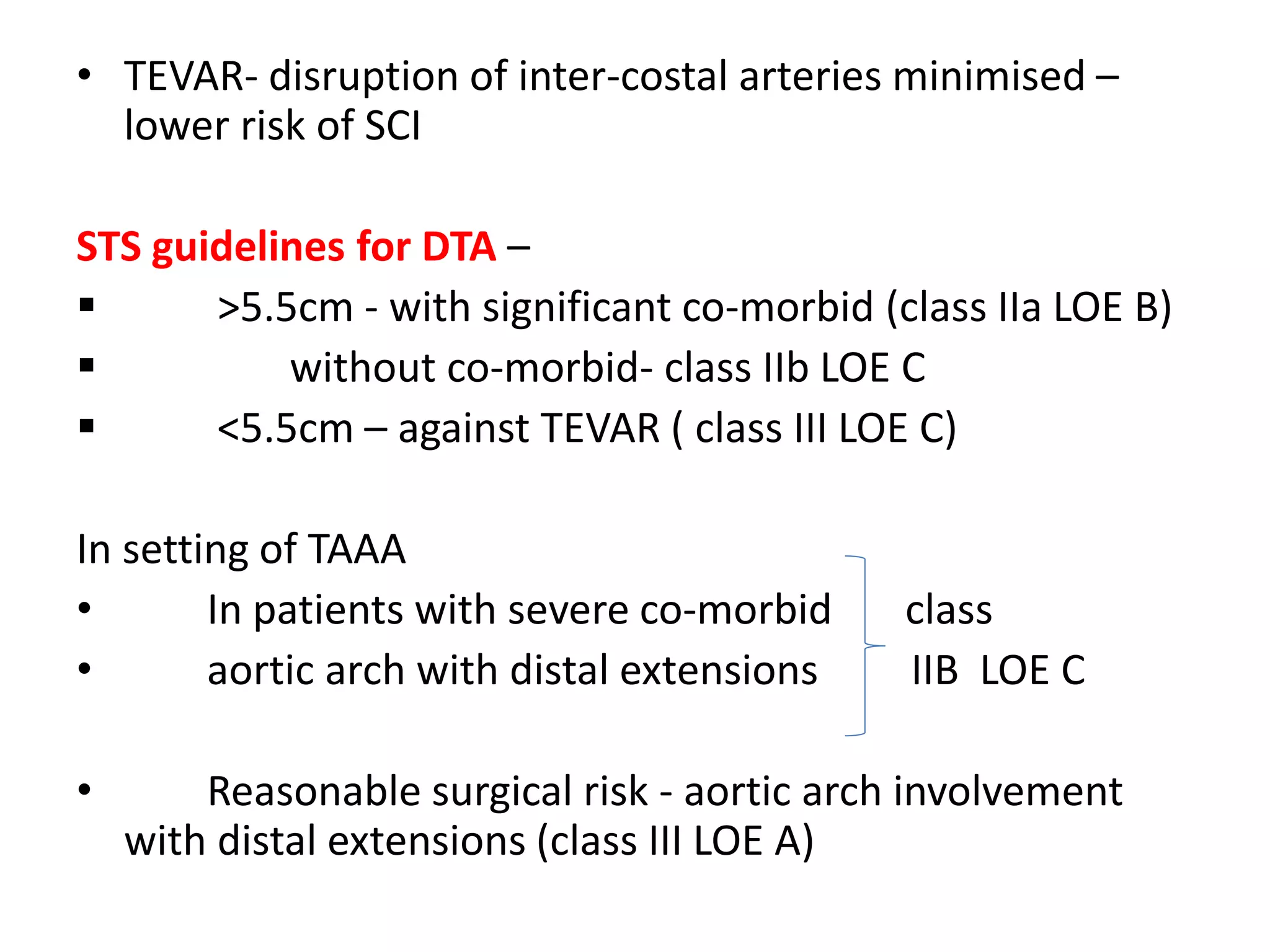
Spinal cord protection is important during aortic surgeries to prevent neurological deficits. The risk is highest with open thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm (TAAA) repair. Techniques to protect the spinal cord include minimizing ischemia time, increasing cord tolerance through hypothermia, augmenting perfusion, and monitoring for ischemia. Early detection of ischemia allows interventions like reattachment of segmental arteries or modifying perfusion to salvage the cord. While endovascular repair reduces risk compared to open surgery, open repair requires strategies like distal aortic perfusion, cerebrospinal fluid drainage and evoked potential monitoring to optimize spinal cord protection.