1. Dr. Rahul Sharma discusses schizophrenia, a mental disorder characterized by disturbances in thinking, behavior, and emotion.
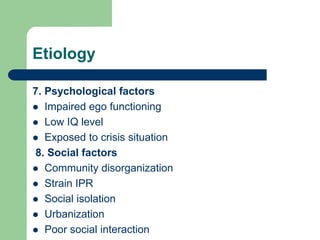
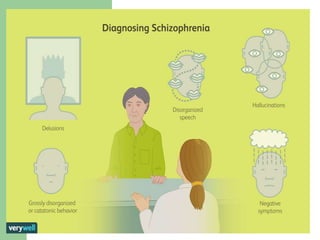
2. Some key causes of schizophrenia discussed are genetic factors and neurodevelopmental issues. Symptoms include hallucinations, delusions, and disorganized speech.
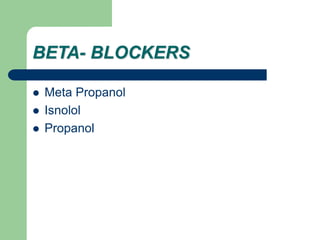
3. There are several types of schizophrenia described, including paranoid, catatonic, and undifferentiated. Diagnosis involves collecting a history and doing a mental status exam. Treatment involves antipsychotic medication as well as psychotherapy.