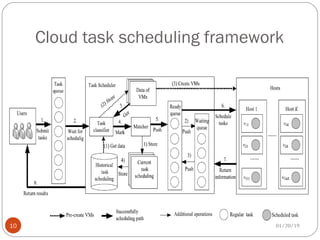
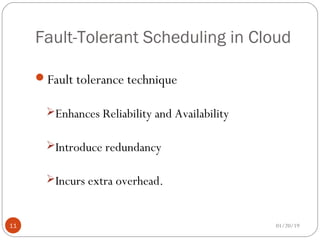
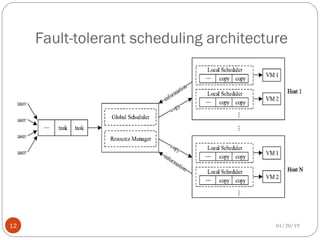
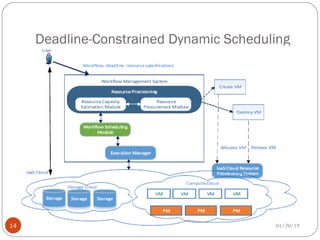
The document discusses various scheduling techniques in cloud computing. It begins with an introduction to scheduling and its importance in cloud computing. It then covers traditional scheduling approaches like FCFS, priority queue, and shortest job first. The document also presents job scheduling frameworks, dynamic and fault-tolerant scheduling, deadline-constrained scheduling, and inter-cloud meta-scheduling. It concludes with the benefits of effective scheduling in improving service quality and resource utilization in cloud environments.


![Traditional Cloud Scheduling [cont..]
Shortest Job First Scheduling
Basis of shortest execution time
Multi Level Feedback Queue Scheduling
Use multiple queue with RR & FCFS.
Multi Level Queue Scheduling
Uses multiple queues with different scheduling.
01/20/195](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/schedulingincloud-190120125656/85/Scheduling-in-cloud-5-320.jpg)





![References [cont..]
5. Stelios Sotiriadis , Nik Bessis, Ashiq Anjum, and Rajkumar Buyya, An Inter-
Cloud Meta-Scheduling (ICMS) Simulation Framework: Architecture and
Evaluation, IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SERVICES COMPUTING, VOL.
11, NO. 1, JANUARY/FEBRUARY 2018.
6. MIAN GUO, QUANSHENG GUAN, AND WENDE KE, Optimal Scheduling
of VMs in Queuing Cloud Computing Systems With a Heterogeneous
Workload, IEEE ACCESS 2018.
7. Ruiting Zhou , Zongpeng Li, and Chuan Wu,Scheduling Frameworks for Cloud
Container Services, IEEE/ACM TRANSACTIONS ON NETWORKING,
VOL. 26, NO. 1, FEBRUARY 2018
8. Arnav Wadhonkar , Deepti Theng ,A Survey on Different Scheduling
Algorithms in Cloud Computing, International Conference on Advances in
Electrical, Electronics, Information, Communication and Bio-Informatics
(AEEICB16).
01/20/1919](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/schedulingincloud-190120125656/85/Scheduling-in-cloud-19-320.jpg)