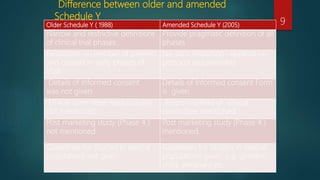
The document outlines the key aspects of Schedule Y, the law in India governing clinical trials. It discusses what Schedule Y is, its purpose, key amendments, and structure. It describes the application process for permission to conduct clinical trials and guidelines around phases of trials, special populations, informed consent, responsibilities of sponsors, investigators and ethics committees, and post-marketing surveillance. Appendices provide more details on required documents, reports, and data.