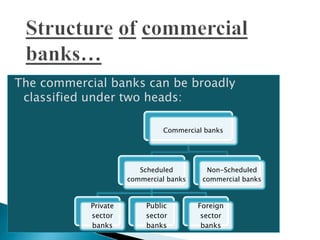
Commercial banks collect savings from depositors and lend money to borrowers. They accept various types of deposits like demand deposits, fixed deposits, and savings deposits. Commercial banks also provide other services like loans, overdraft facilities, bill discounting, and collection of payments. They play an important role in capital formation, providing finance and credit, promoting entrepreneurship, and balanced regional development. Commercial banks in India are classified as scheduled commercial banks, which include public sector banks, private sector banks, and foreign banks, or non-scheduled commercial banks.