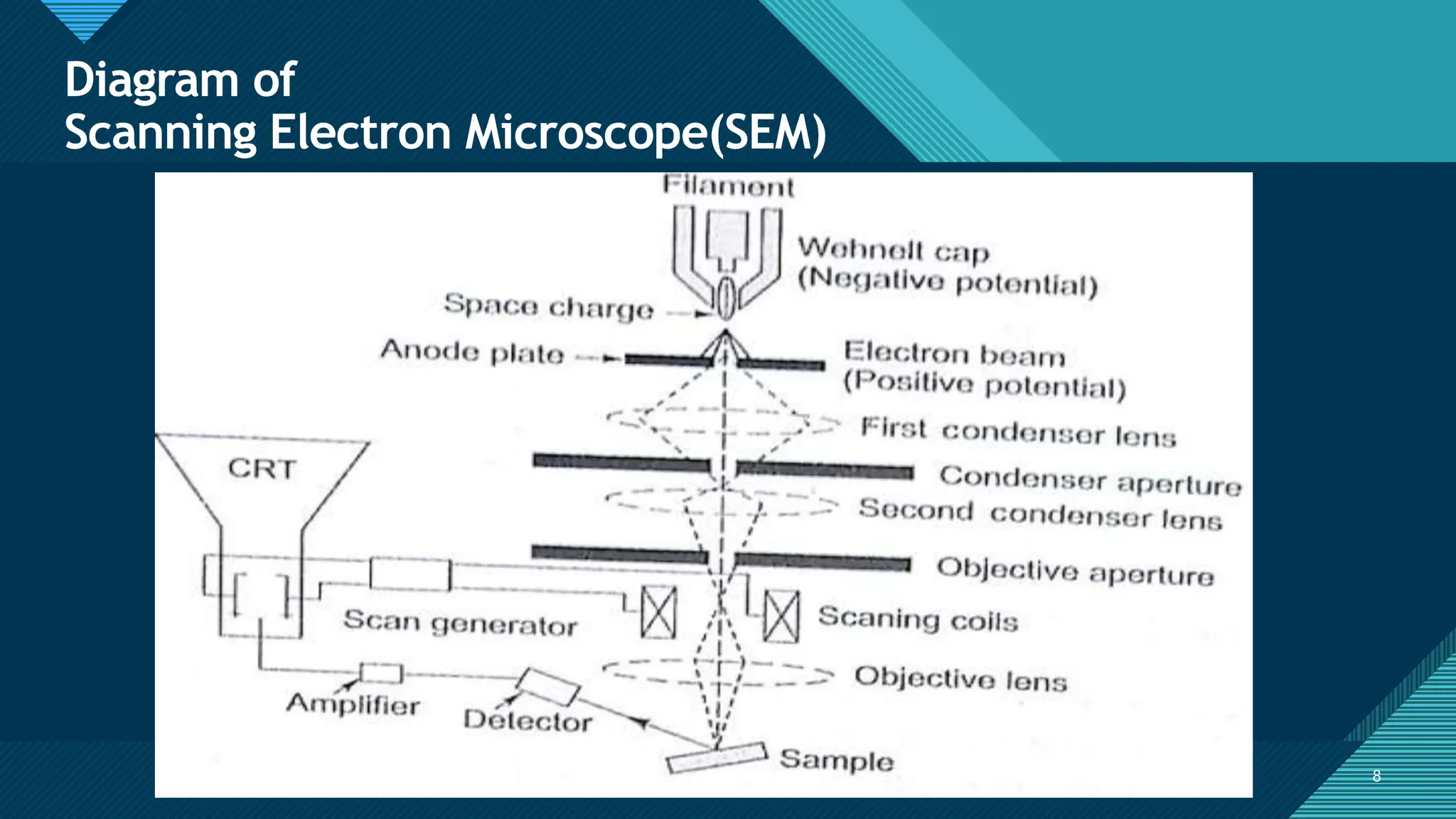
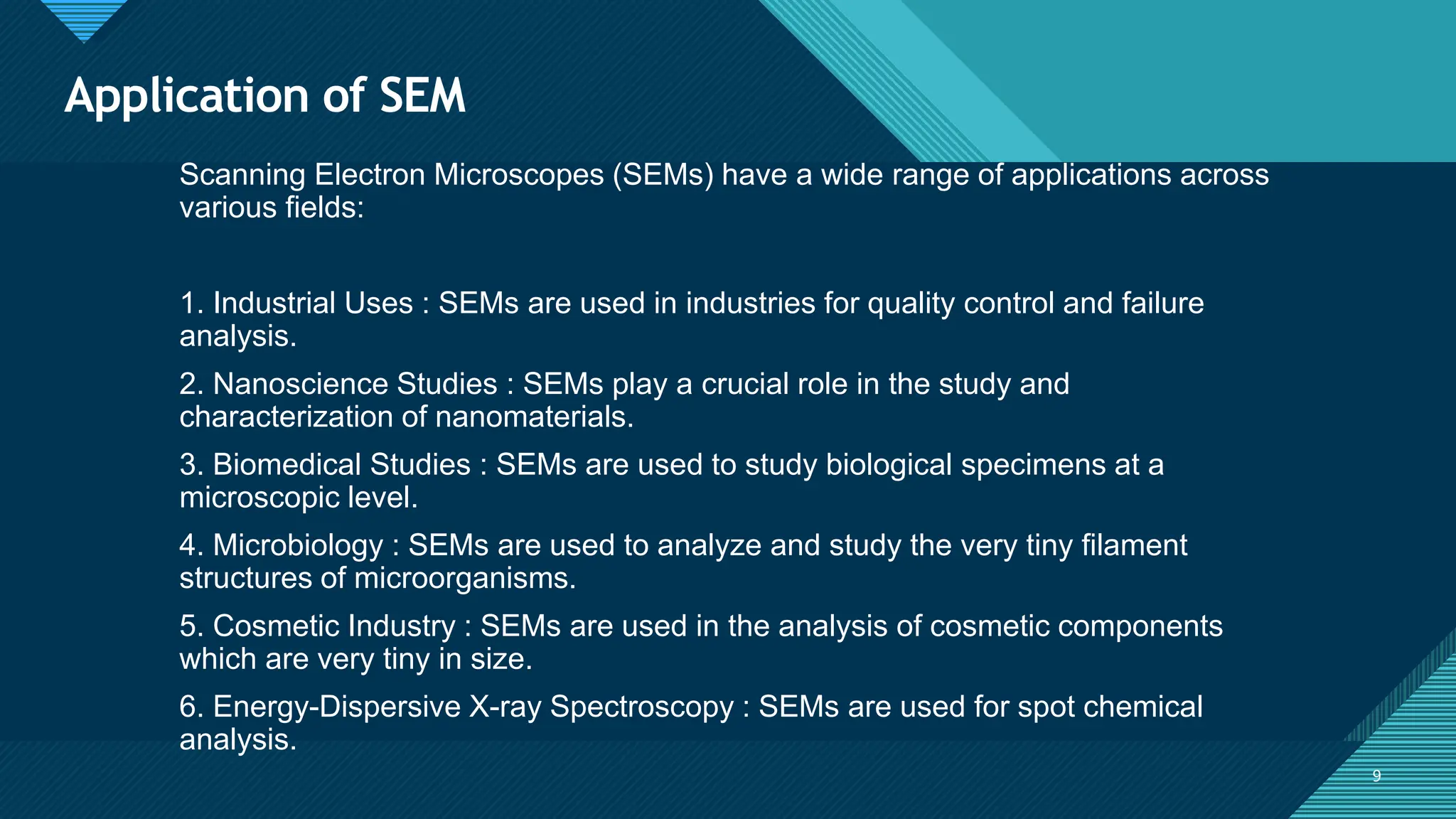
The document summarizes the scanning electron microscope (SEM). It describes that the SEM uses a low-energy electron beam to scan microorganisms, providing higher resolution images than light microscopes. The SEM works by using kinetic energy to generate signals from secondary and backscattered electrons emitted from the specimen when interacted with by the electron beam. These signals are used to create three-dimensional images showing the specimen's topography, morphology, composition, and crystallographic structure. Applications of the SEM include industrial quality control, nanoscience, biomedical studies, microbiology, and cosmetic analysis.
![Click to edit Master title style
1
Seminar on
Scanning
Electron
Microscope
(SEM)
Kongu Engineering College
By: Kavin Kumar S
[23MER015]
Hariprathap G K K
[23MER011]
Date:05.01.2024](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scanningelectronmicroscopeppt-240113172657-0b13c5fc/75/Scanning-electron-microscope-ppt-pptx-1-2048.jpg)