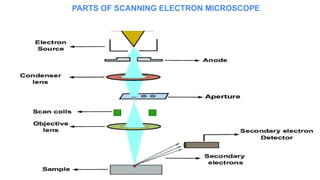
The document provides an overview of scanning electron microscopes (SEM), detailing their development, principles, components, applications, advantages, and disadvantages. SEMs offer improved resolution over traditional light microscopes and are used in various fields including microbiology and nanoscience for detailed surface analysis. Despite their high cost and the need for specialized training, SEMs are user-friendly and can quickly generate data for analysis.