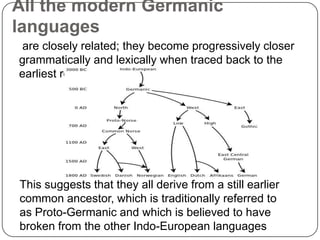
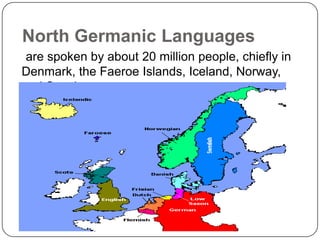
The North Germanic languages, also called Scandinavian languages, are spoken by about 20 million people in Scandinavia. They include Norwegian, Danish, Swedish, Icelandic, and Faroese. These languages share several distinctive grammatical features like adding definite articles as suffixes to nouns. While they derive from a common Proto-Germanic ancestor and share many sound changes, political and cultural developments over time have led to some differences in vocabulary between the languages. The oldest written records that show features of Scandinavian languages are runic inscriptions from the 8th to 11th centuries, while manuscripts in Latin script from the 12th century on provide more materials in Old Norse, the main representative of the older forms of these languages.