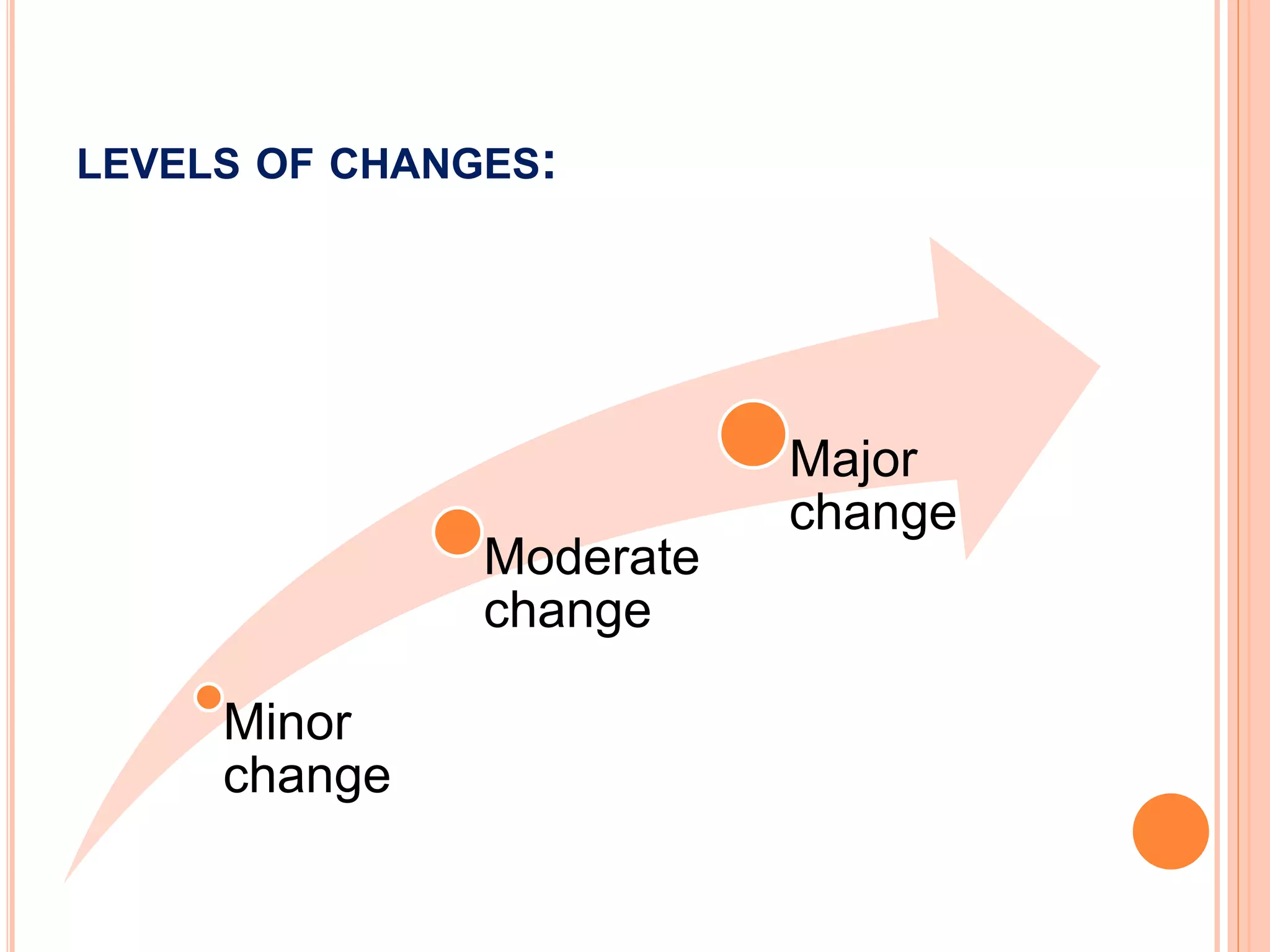
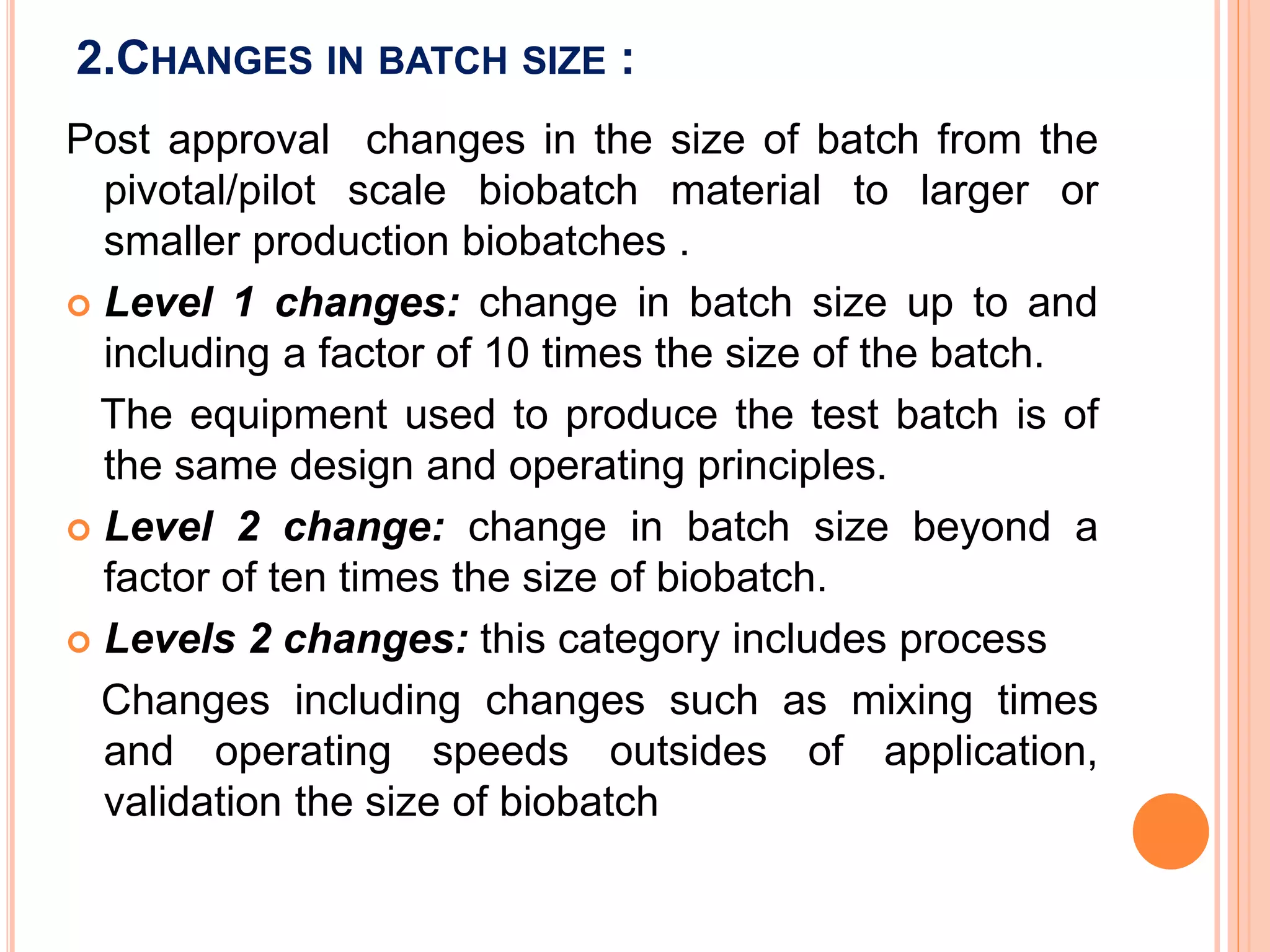
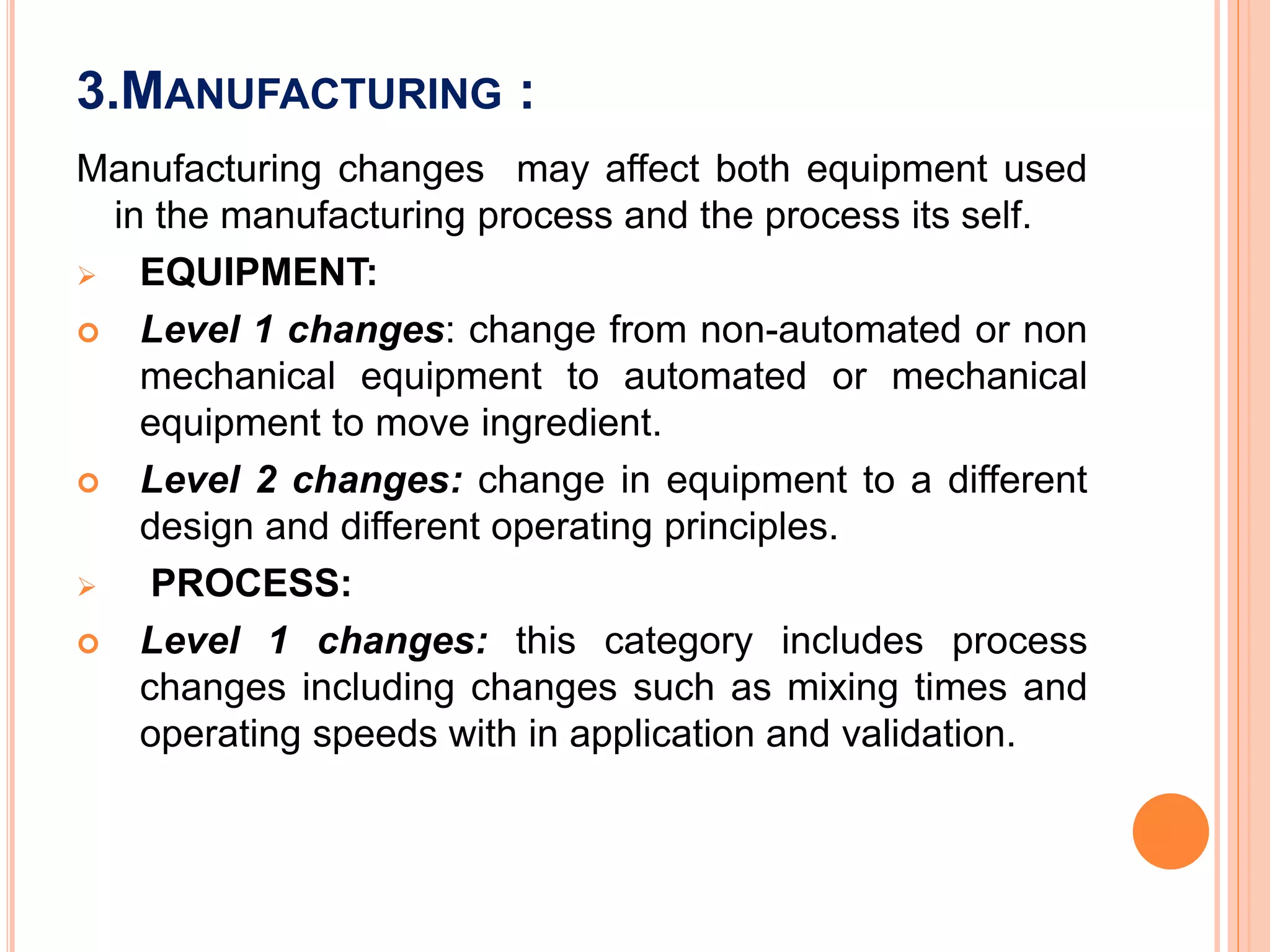
Scale up and post approval changes (SUPAC) involve changes made after drug approval to manufacturing processes, equipment, batch size, or sites. Changes are classified as minor, moderate, or major. Site changes include those within a single facility or between adjacent facilities (Level 1) or different campuses (Level 3). Batch size changes up to 10 times the initial size are Level 1, and beyond that are Level 2. Equipment changes include automated vs non-automated (Level 1) or different designs (Level 2). Process changes include altered parameters within validated ranges (Level 1).
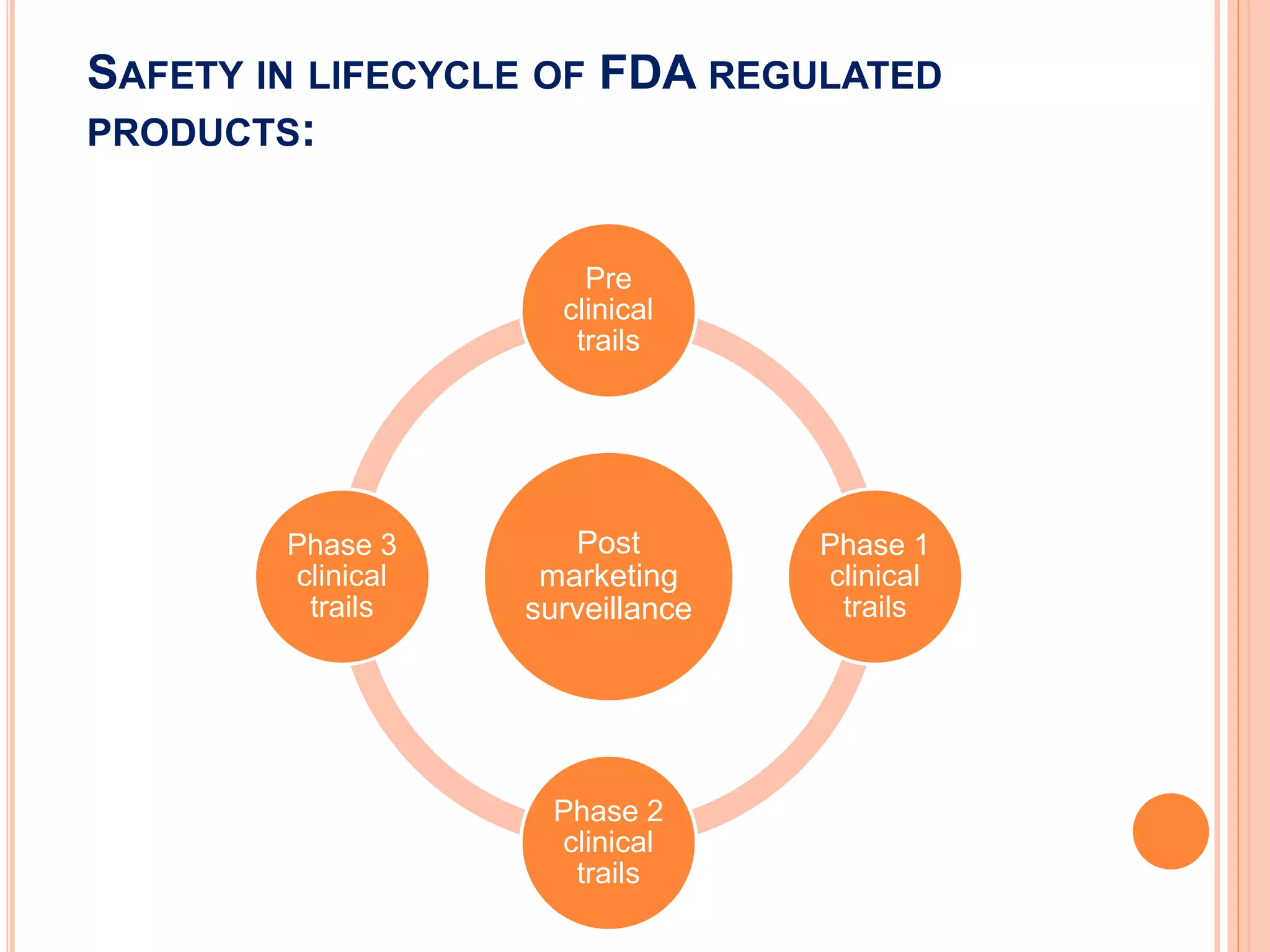
Post marketing surveillance monitors drug safety after approval and includes adverse event reporting, re-examination of drugs, and re-evaluation of risk-benefit profiles