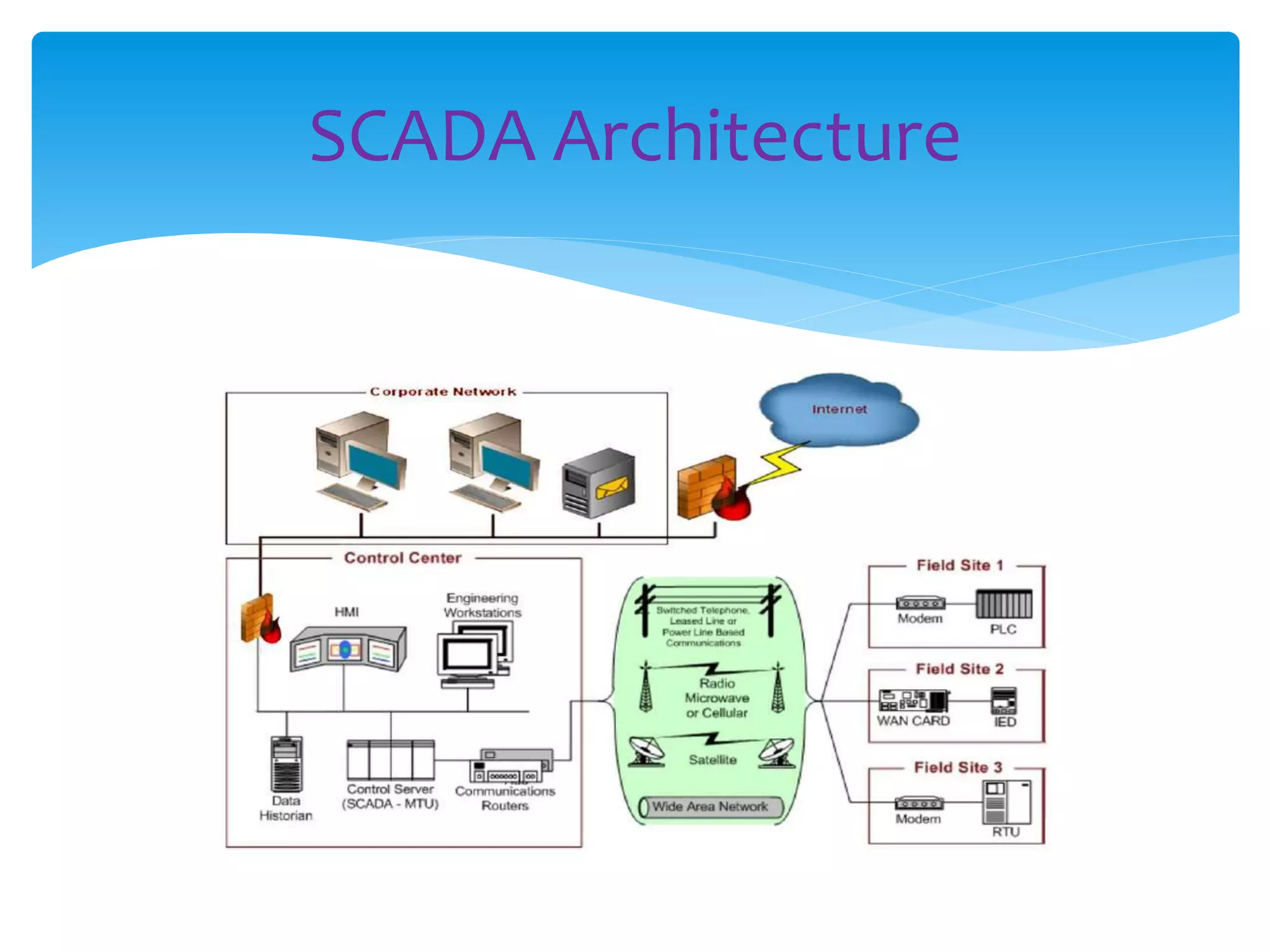
SCADA (Supervisory Control Data Acquisition) systems collect and manage data from remote devices across various industries, including power generation and manufacturing. The system architecture consists of a control center, field sites, and communication links, facilitating real-time data collection and analysis. Key components include the Master Terminal Unit (MTU), Human Machine Interface (HMI), Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC), and Intelligent Electronic Devices (IED), contributing to enhanced monitoring, control, and maintenance.