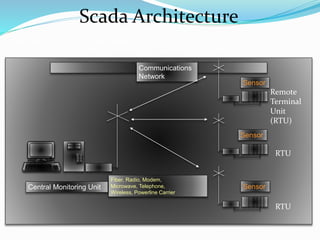
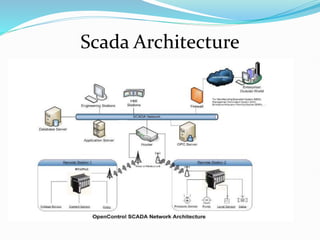
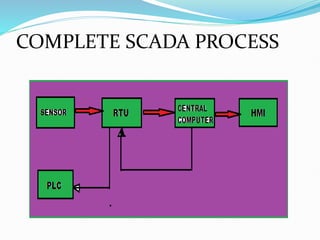
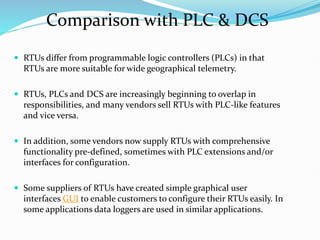
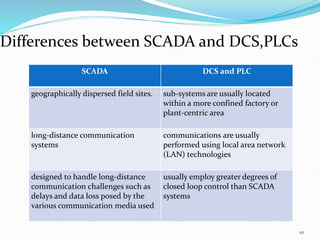
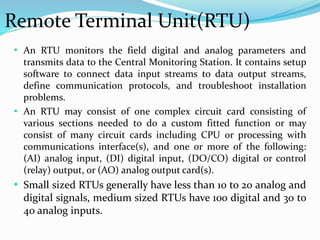
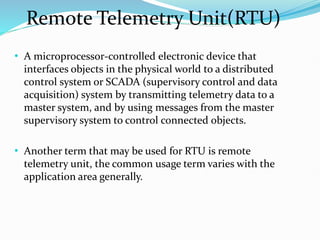
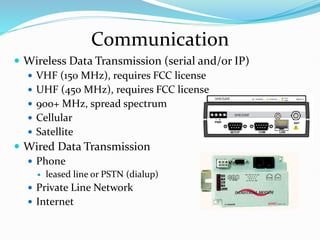
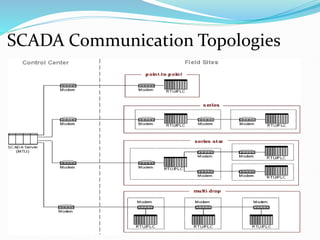
SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems are used to centrally monitor and control remote equipment and industrial processes. They allow for remote data collection, control of processes from a distance, creation of logs and reports, and sending of real-time information to engineers and operators. SCADA systems are used to control processes in industries like oil and gas, manufacturing, water treatment, and electricity. They consist of remote terminal units that collect field data, master control units that process information and send control signals, and communication networks connecting all components.