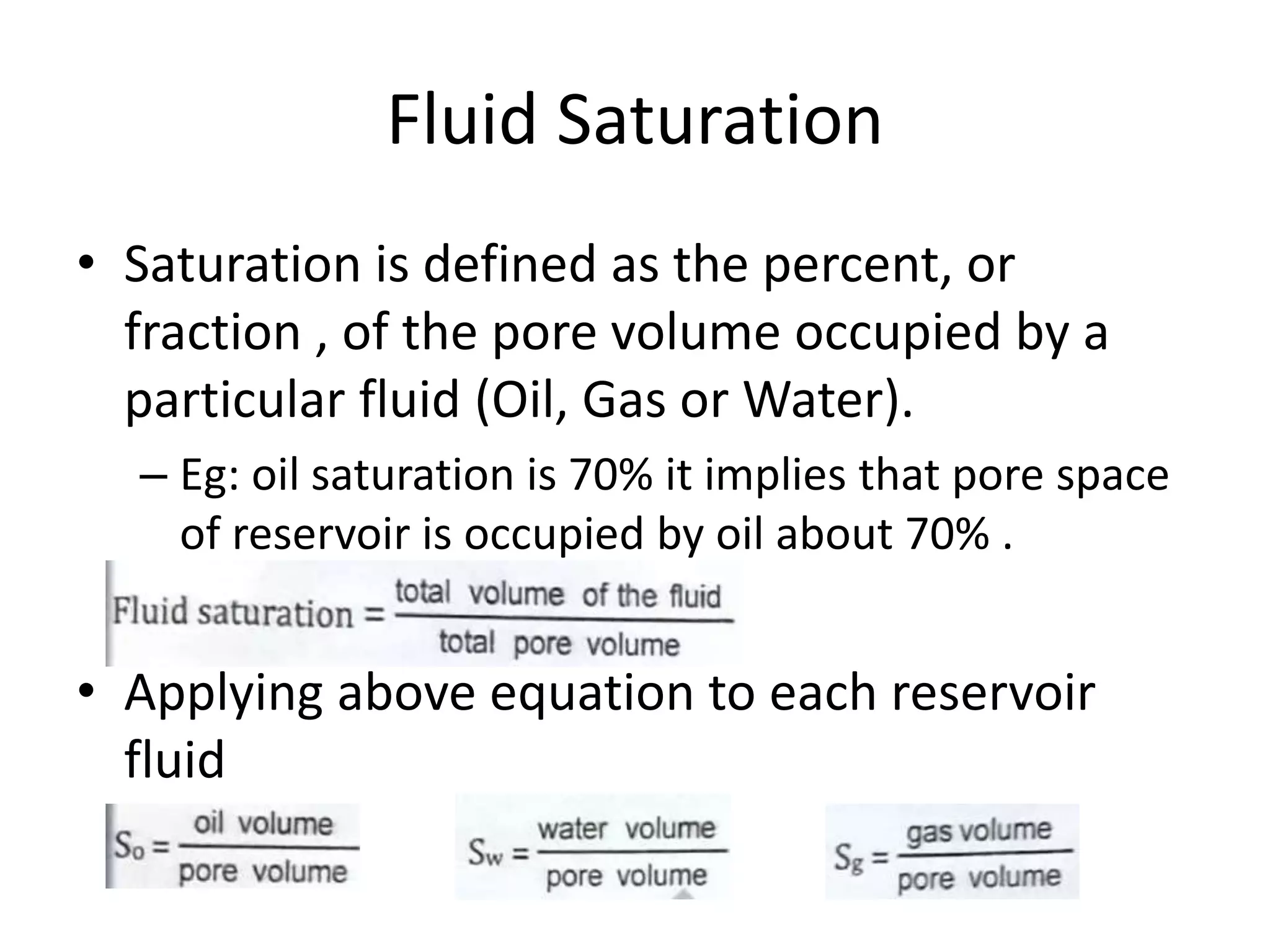
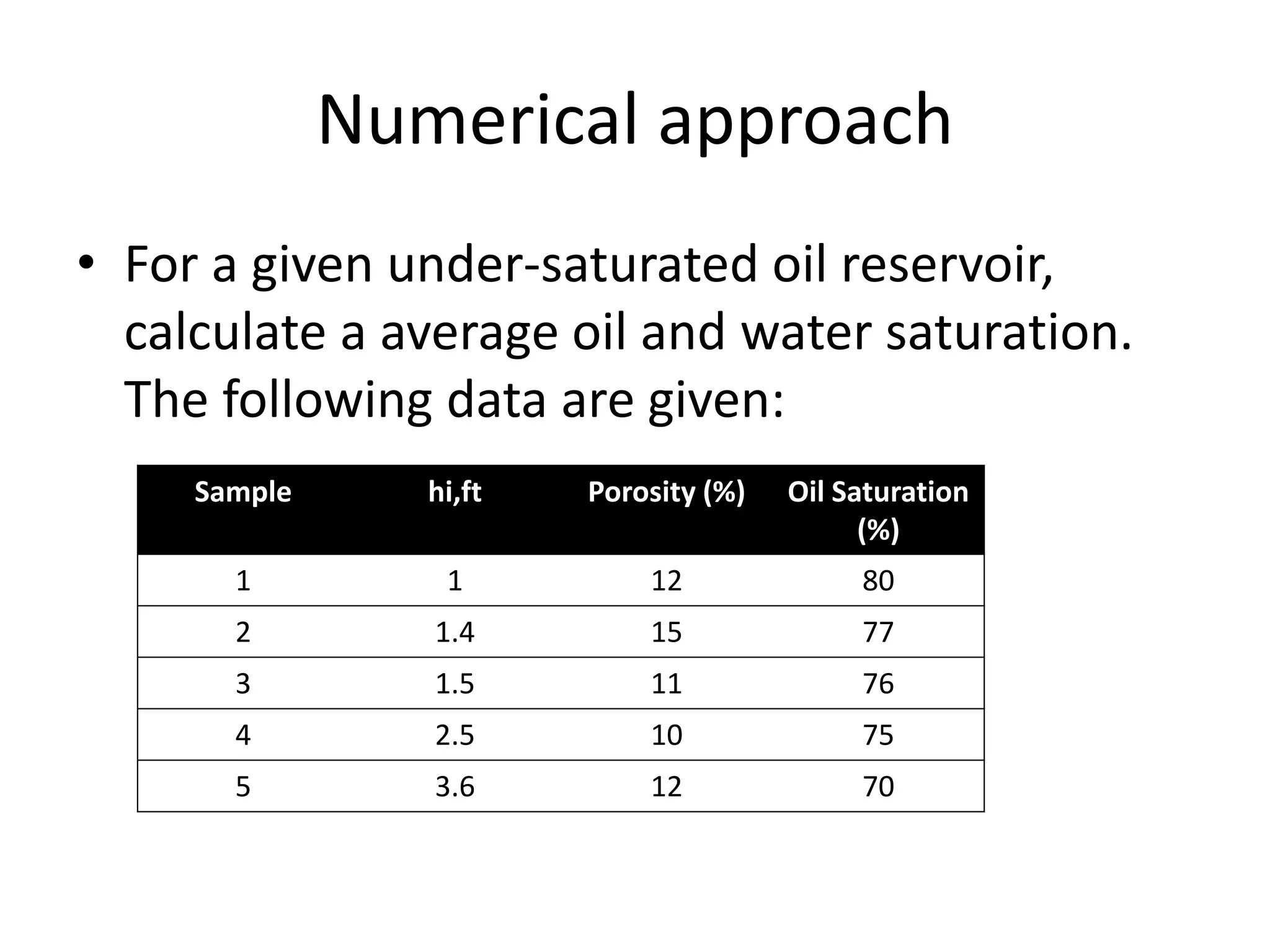
This document discusses petro-physical properties of reservoirs, including definitions of key concepts like fluid saturation, irreducible saturation, critical saturation, and residual saturation. It explains that saturation is defined as the percentage of pore volume occupied by a fluid (oil, gas, or water). It also provides an example of calculating average oil and water saturation for an under-saturated oil reservoir using porosity and oil saturation data from multiple samples. The document concludes by listing references for further reading on petroleum reservoir engineering topics.