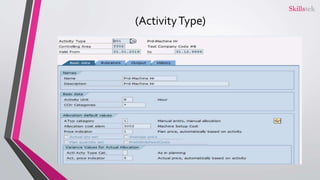
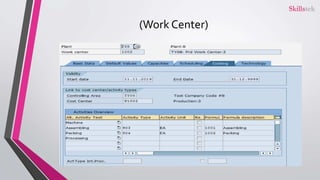
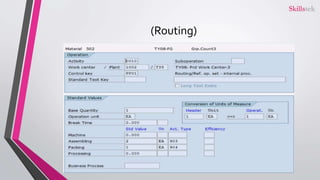
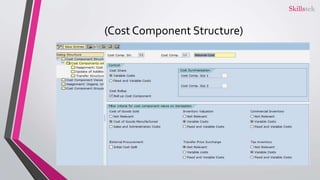
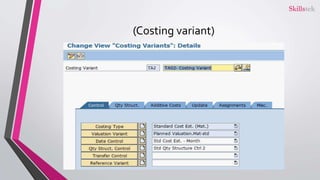
The document provides an overview of SAP product costing, highlighting its importance, core components, and prerequisites. It explains the significance of master data, cost component structure, costing variants, and cost estimates in creating accurate cost calculations for manufactured goods. Additionally, it details the steps needed to implement product costing in SAP, including activating necessary modules and managing relevant data.