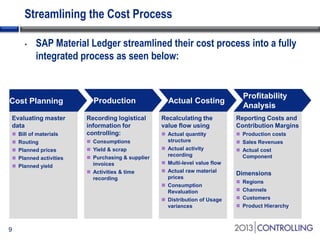
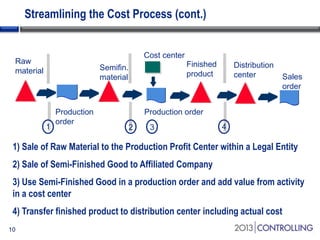
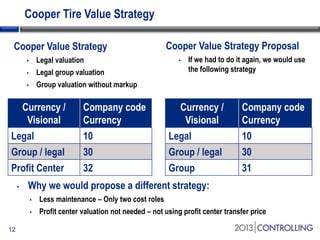
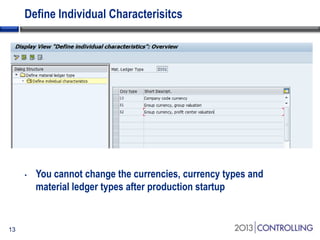
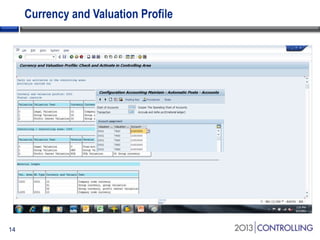
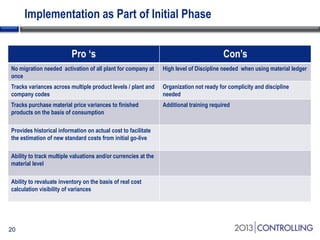
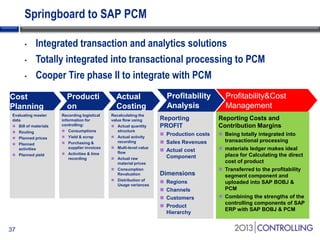
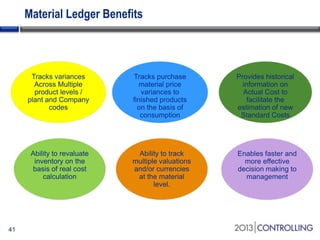
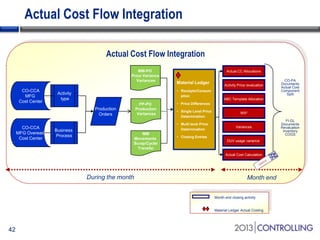
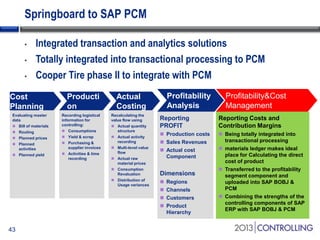
Cooper Tire implemented SAP Material Ledger as part of their initial SAP implementation in order to gain visibility into actual product costs and variances across production processes. Some key lessons learned included making the final decision to implement Material Ledger early, ensuring quality consultant support, and properly configuring for long-term requirements. Material Ledger provided benefits like impact of price variances and actual inventory costs but also challenges like increased data volumes and complexities. Cooper Tire's next steps include further integrating Material Ledger with SAP Profitability and Cost Management for improved cost and profitability reporting and analysis.