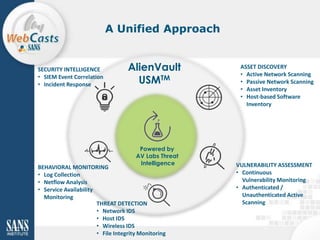
The document discusses the challenges organizations face in improving their security monitoring through SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) systems, emphasizing the importance of threat intelligence integration. It outlines common issues with current SIEM implementations and offers strategies for enhancing their effectiveness, such as thorough planning, ease of use, and leveraging collaborative threat intelligence like AlienVault's OTX. Ultimately, it suggests that with proper planning and questioning of vendors, organizations can successfully implement SIEM without significant obstacles.