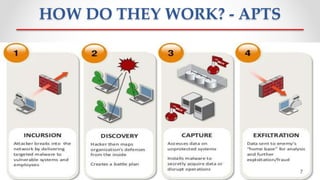
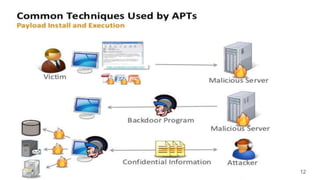
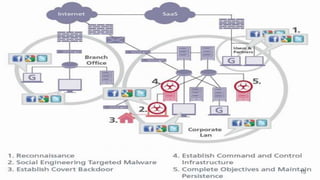
The document discusses Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs), which are sophisticated cyber attacks aimed at gaining long-term access to sensitive information through stealthy methods. It outlines the stages of the APT exploitation cycle from reconnaissance to data exfiltration, along with case studies illustrating successful APT attacks. Various security solutions and preventive measures to mitigate APT risks are also presented, including software solutions like EMET and Bit9 for enhanced protection.




![WHAT IS APT?
• “An advanced and normally clandestine means to gain continual,
persistent intelligence on an individual, or group of individuals”
[Wikipedia]
• “… a sophisticated, mercurial way that advanced attackers can
break into systems, not get caught, keeping long-term access to
exfiltrate data at will.” [McAfee]
• “… a sophisticated and organized cyber attack to access and steal
information from compromised computers.” [MANDIANT]
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ismpresentationmayur-160104044459/85/Advanced-Persistent-Threats-APTs-Information-Security-Management-5-320.jpg)