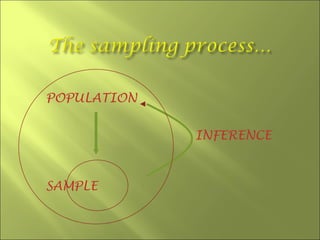
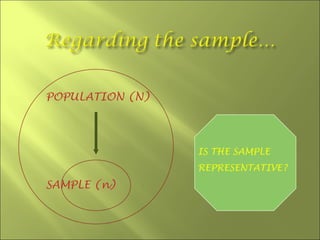
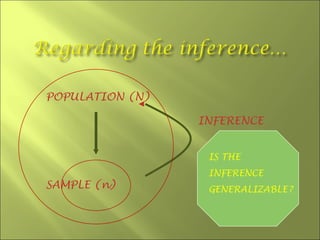
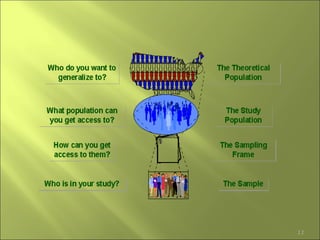
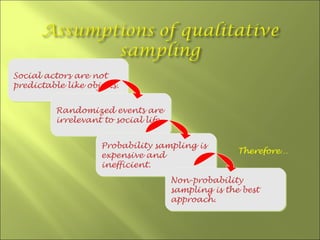
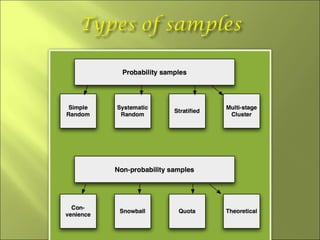
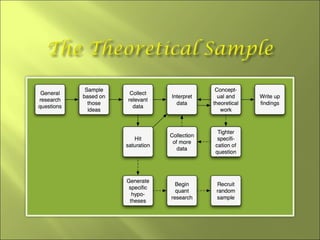
This document discusses key concepts related to sampling in research studies. It defines population as the larger group being studied, and sample as the subset of individuals selected for a study. There are different types of sampling methods discussed, including probability sampling which allows calculation of sampling error, and non-probability sampling which is less expensive but does not allow generalization. The document emphasizes that sample size depends on achieving saturation in qualitative research versus statistical validity in quantitative research. Sources of error like sampling error and bias are also outlined.