Embed presentation
Downloaded 529 times






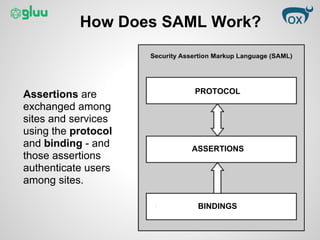
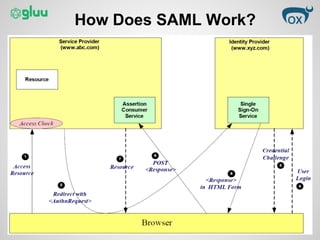
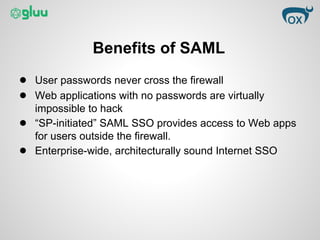



This document provides an overview of the Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) protocol. SAML allows sites to exchange user authentication, authorization, and attribute information via XML messages. It enables single sign-on, single logout, and attribute sharing across applications. SAML 2.0 uses standards like XML, HTTP, and SOAP to standardize single sign-on across enterprise cloud apps. It works by exchanging assertions about users via protocols and bindings to authenticate users among sites. Benefits include centralized identity control and single sign-on without exposing passwords.










