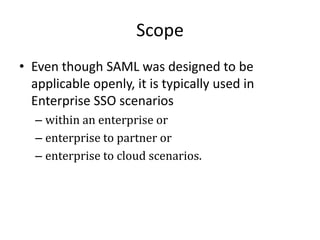
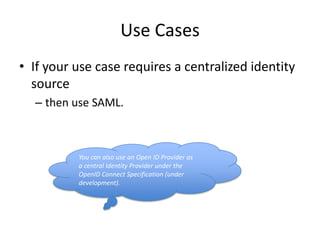
SAML and OAuth are both standards for authentication and authorization but have key differences. SAML is an XML standard that enables single sign-on, federation, and identity management through security assertions. OAuth is a standard for authorization that allows secure access to internet resources without sharing passwords. While SAML uses XML tokens and supports SOAP/JMS transport, OAuth uses HTTP and JSON/binary tokens. SAML is commonly used for enterprise SSO and identity federation, while OAuth is designed for authorization of internet resources from applications. The document recommends using SAML for SSO and OAuth for delegated access to resources.