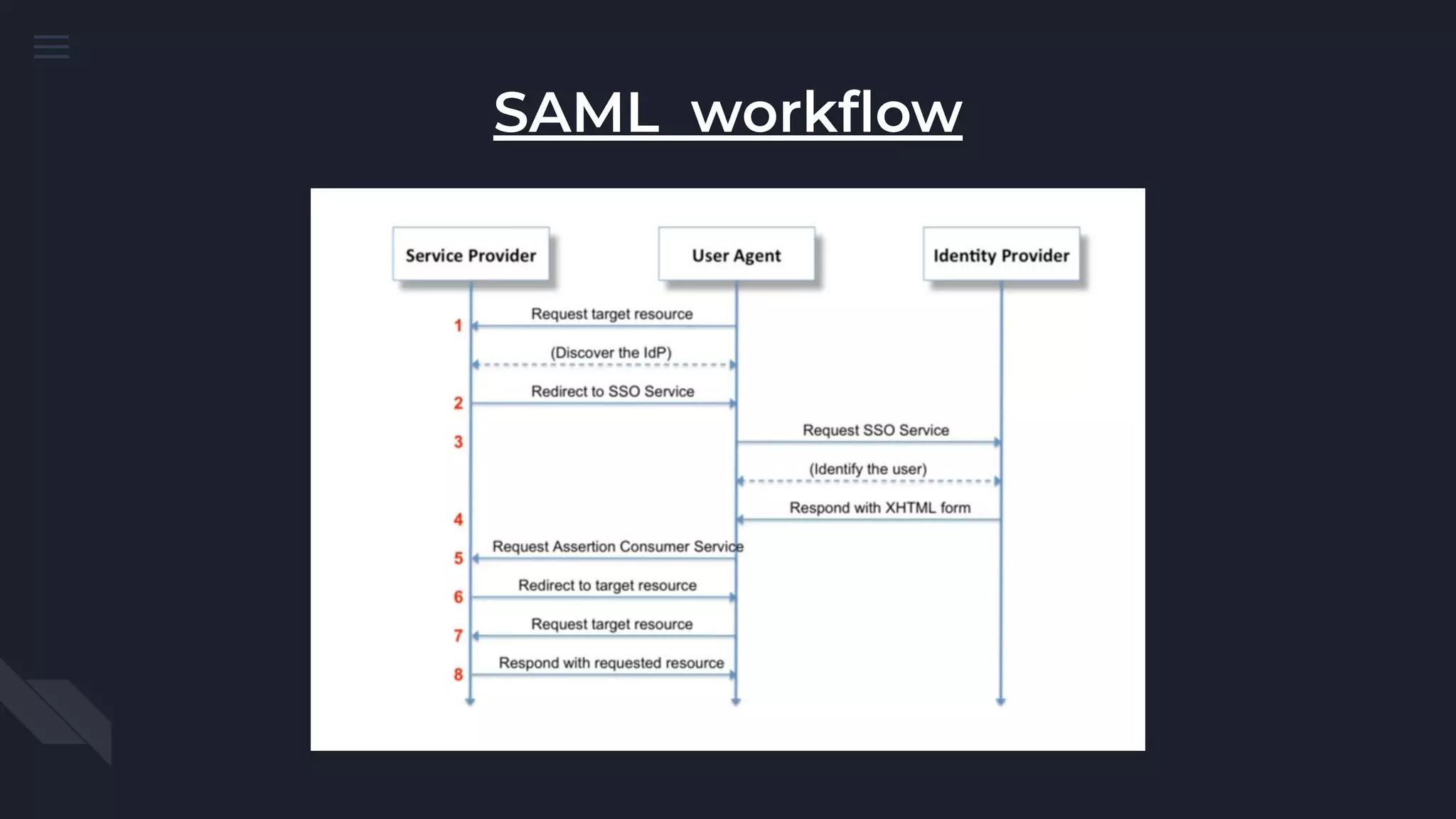
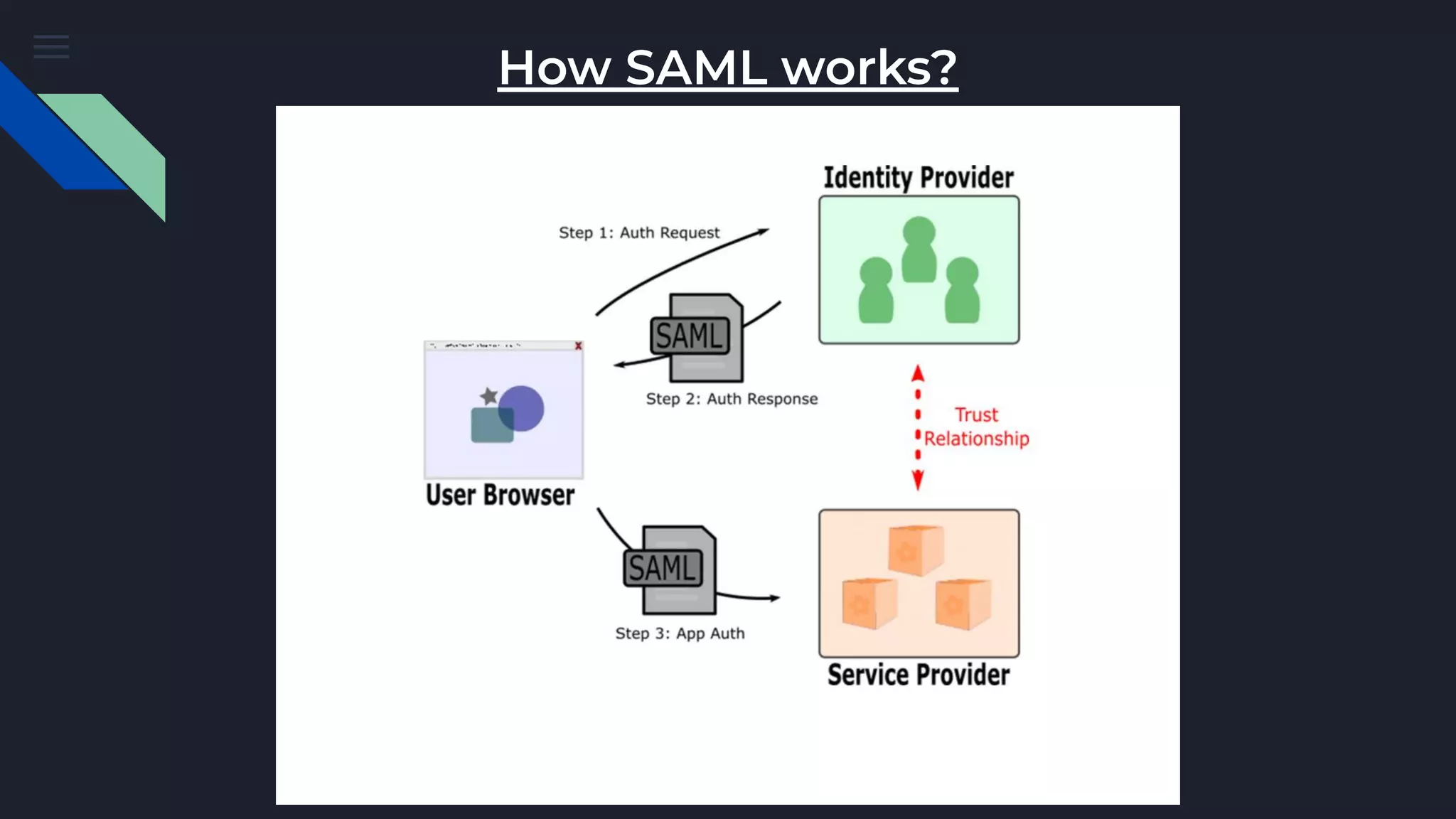
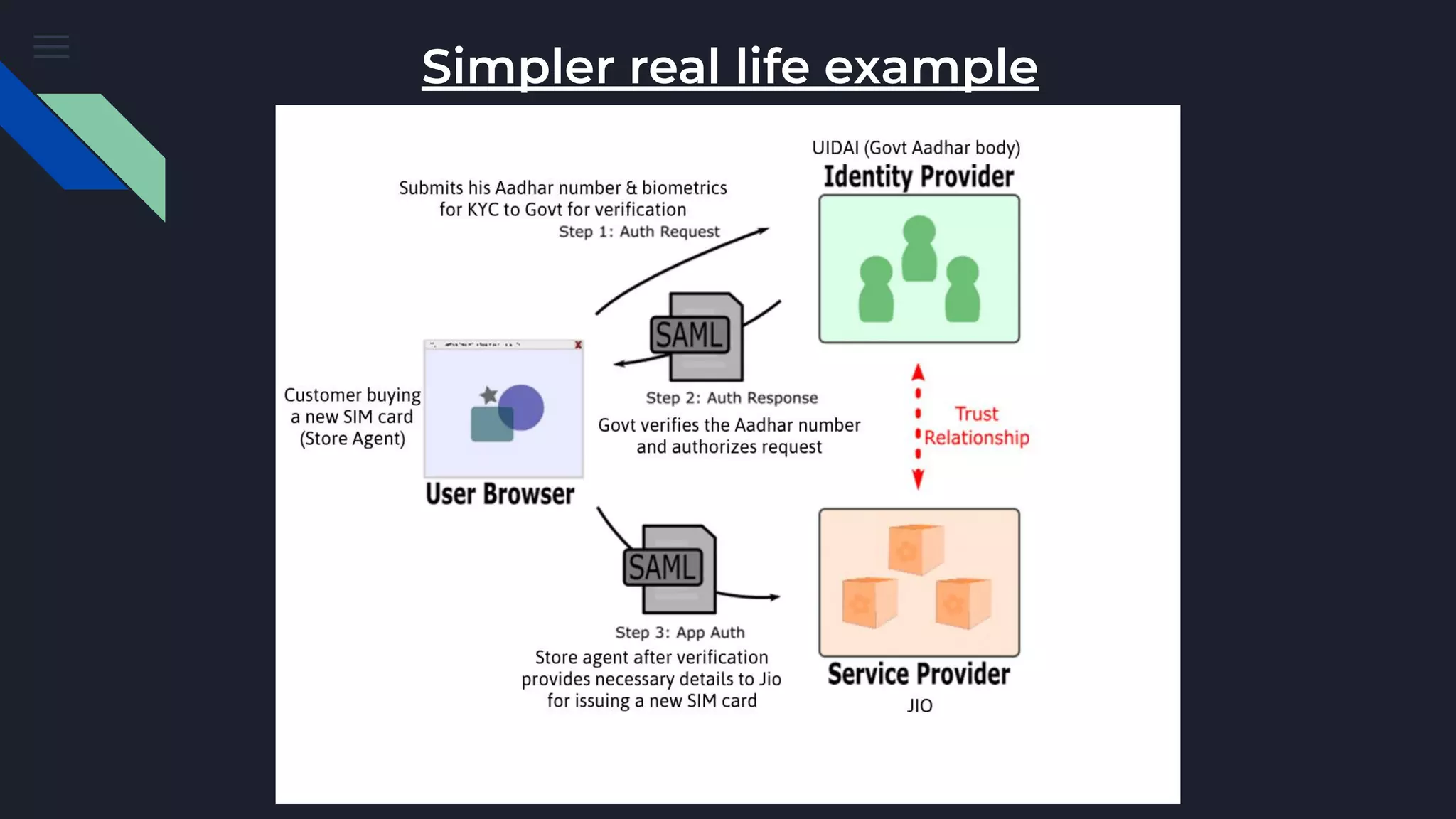
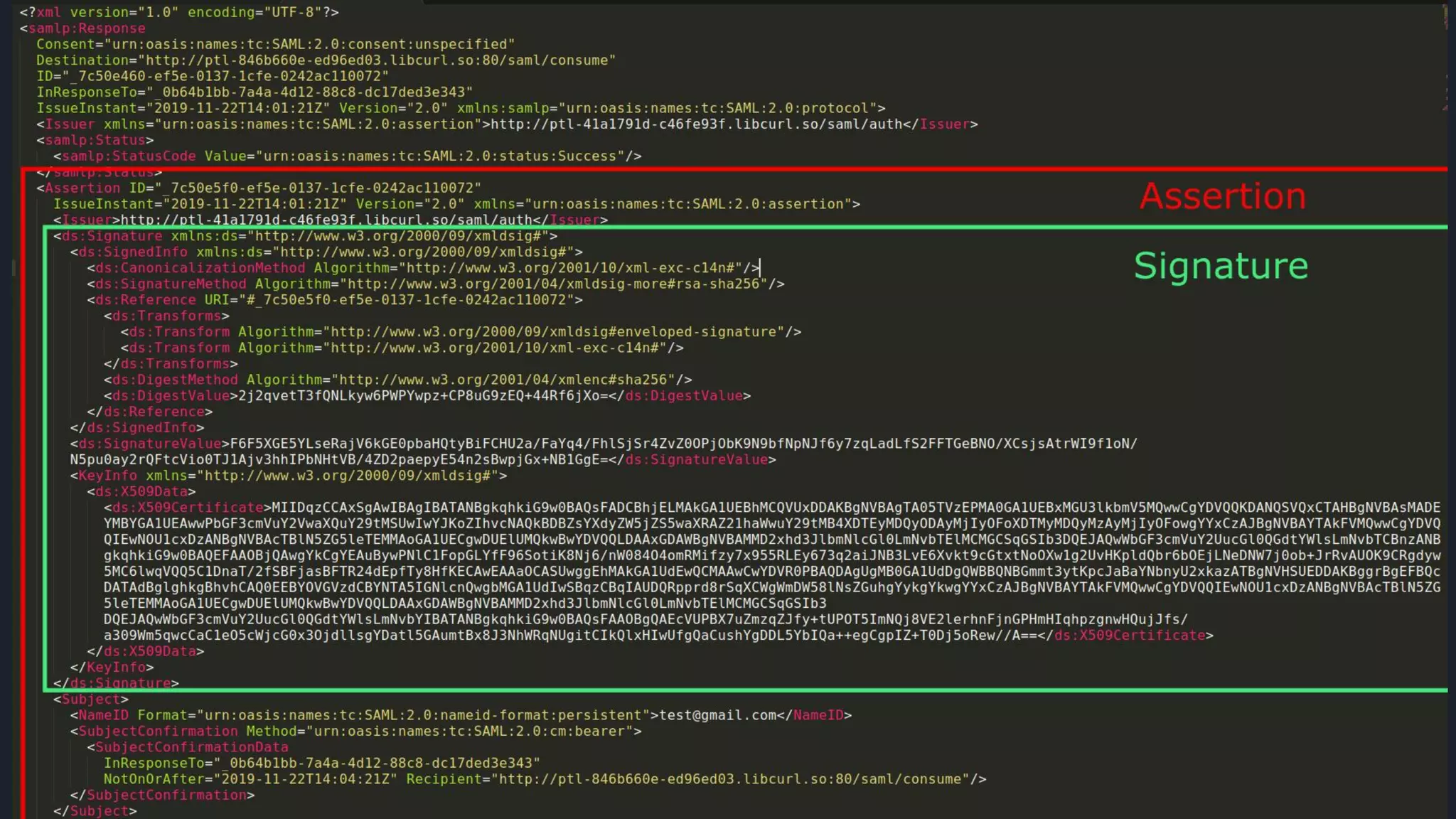
The document discusses Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML), which is an open standard for exchanging authentication and authorization data between identity providers and service providers. It highlights the vulnerabilities associated with SAML and Single Sign-On (SSO) implementations, such as account takeover and privilege escalation, often due to misconfigurations. The text emphasizes the security implications of broken SAML workflows and common mistakes in SAML implementations.