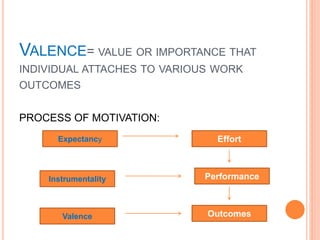
A salesperson's motivation is determined by their expectations, the instrumentality of their actions, and the valence they place on potential outcomes. It is also influenced by personal characteristics, environmental factors, and organizational policies. A salesperson's motivation changes throughout their career as they progress from exploration to establishment to maintenance stages. Organizations can impact motivation through leadership, compensation plans, and managing environmental challenges.