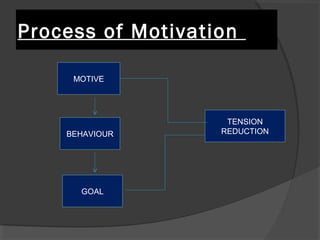
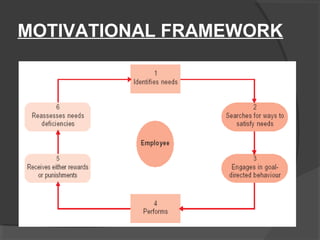
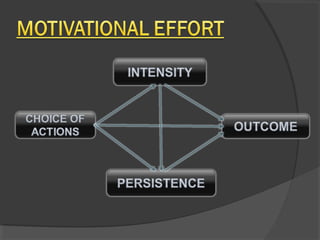
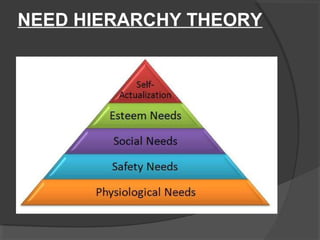
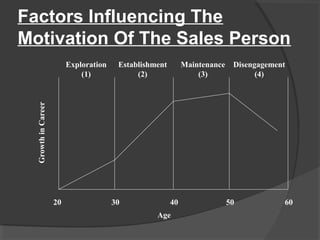
This document discusses motivation of salespeople. It defines motivation as the driving force that causes individuals to work towards goals to fulfill needs. For salespeople specifically, motivation is the effort they put into their jobs. The document then discusses different theories of motivation including need hierarchy theory, Herzberg's two-factor theory, ERG theory, and goal setting theory. It also outlines different financial and non-financial rewards that can be used to motivate salespeople. Finally, it discusses factors that influence salesperson motivation over the course of their career.