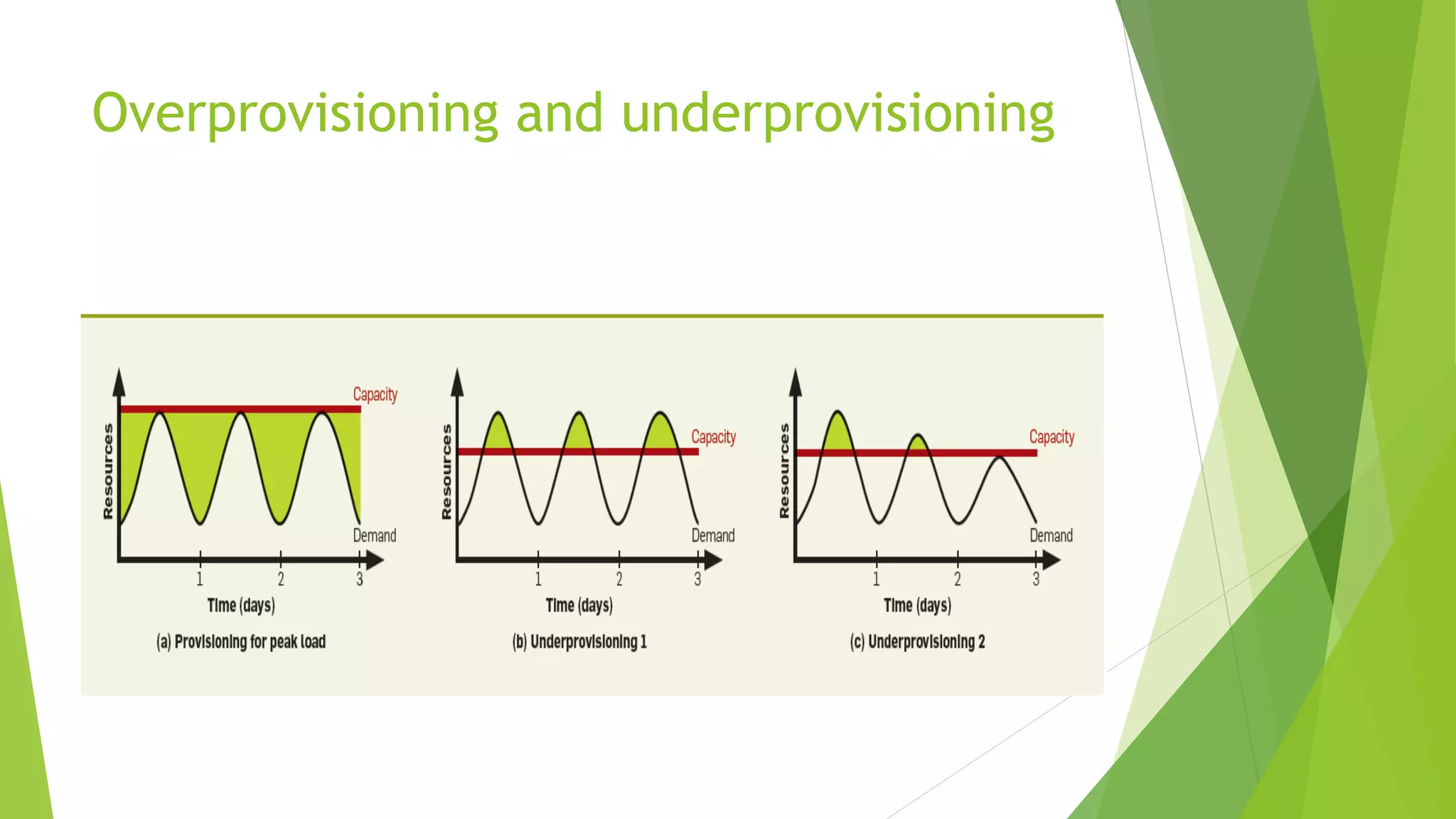
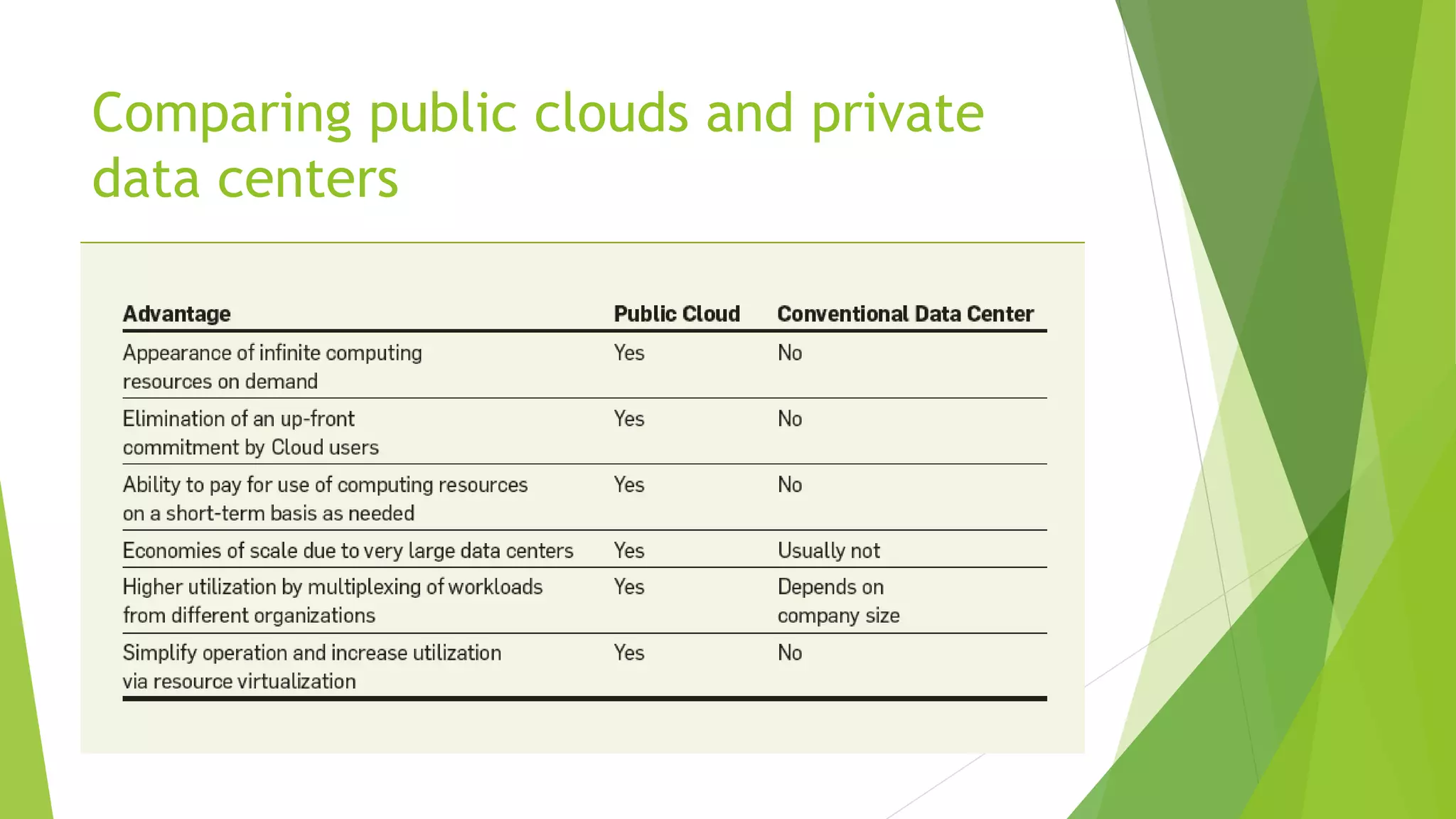
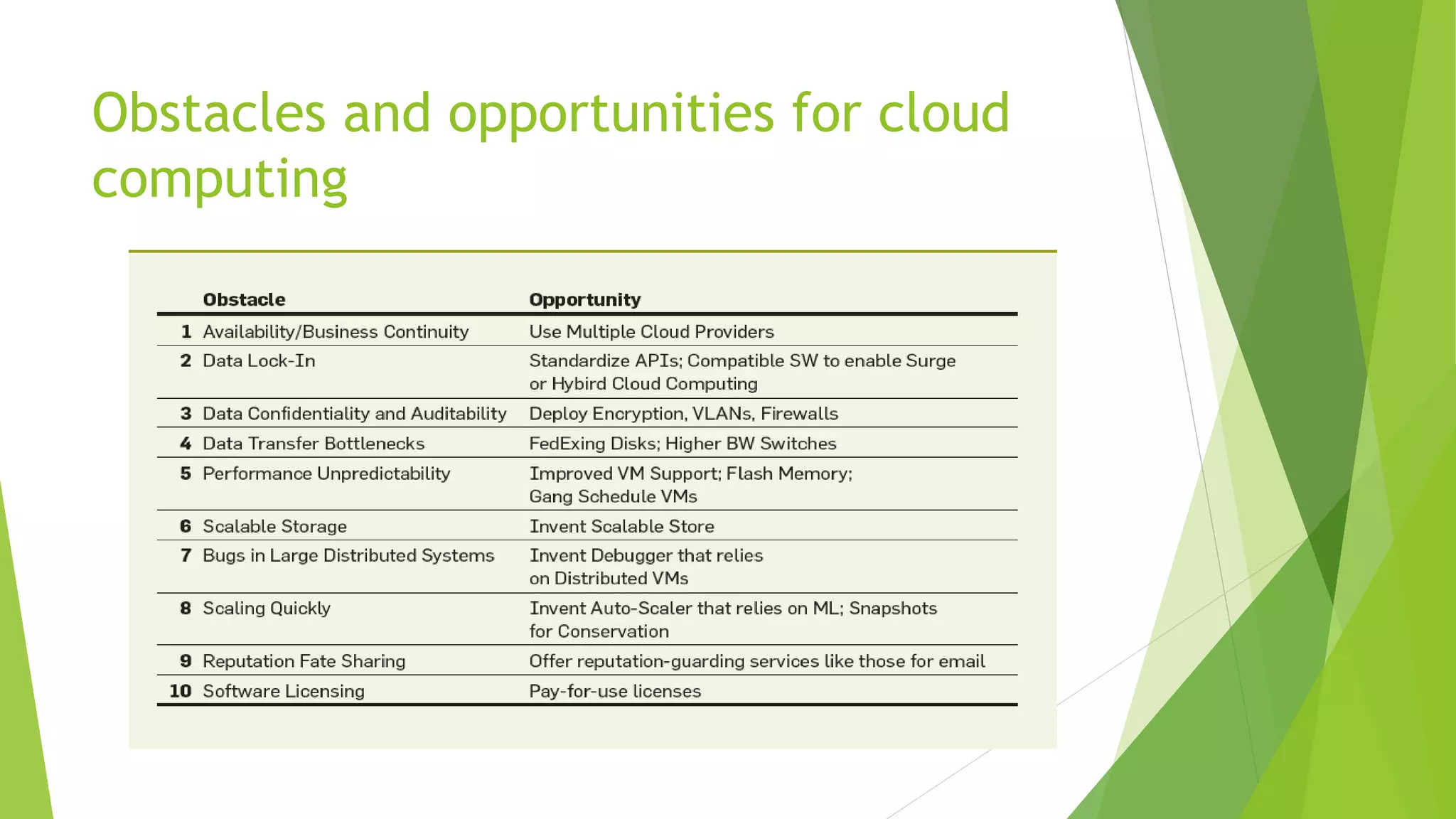
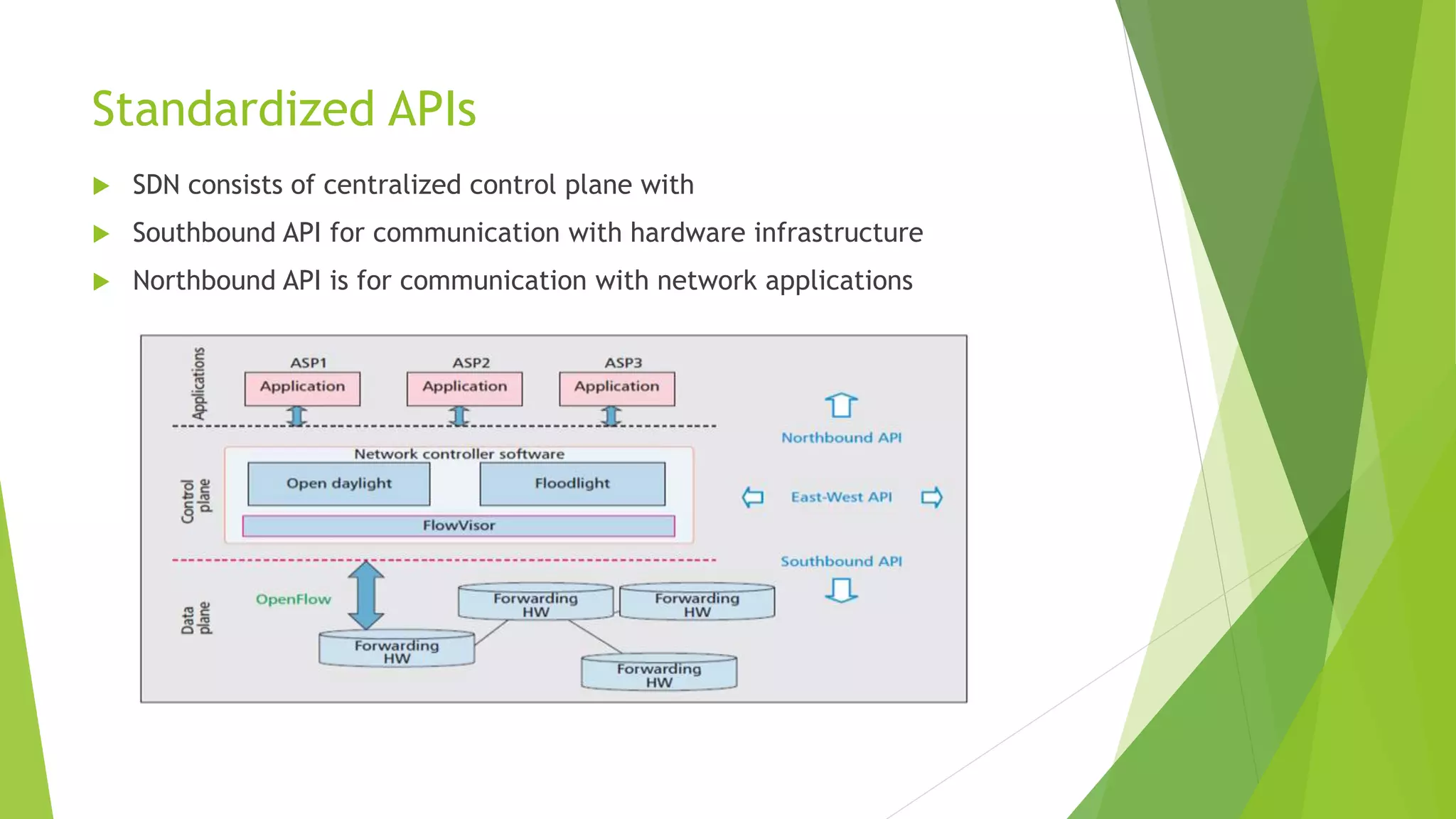
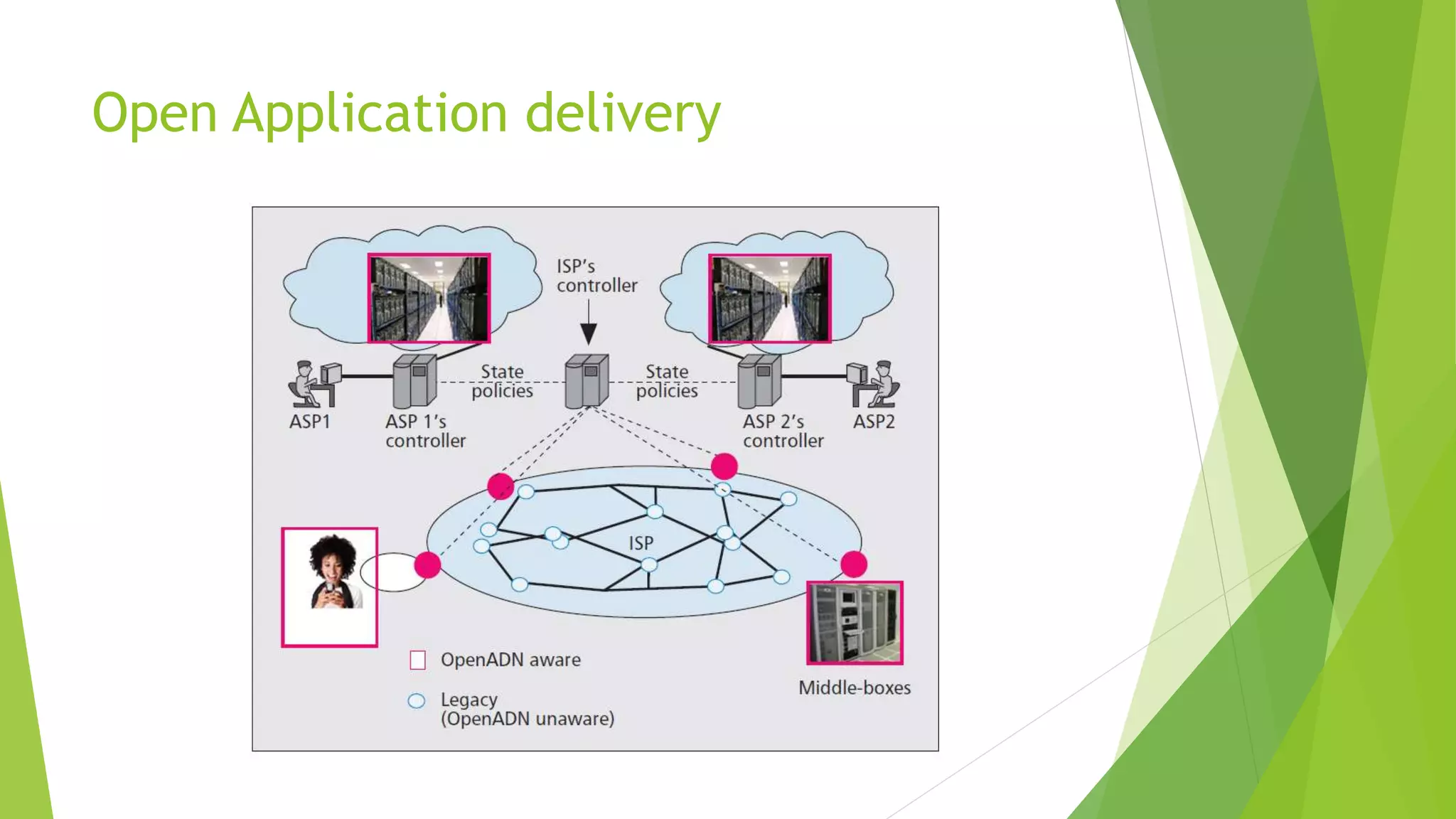
The document presents a graduate presentation on cloud computing, network virtualization, and software-defined networking, highlighting key concepts and innovations in these fields. It covers various aspects such as the definitions of public and private clouds, virtualization in computing, and the separation of control and data planes in software-defined networking. Additionally, it discusses the challenges and opportunities in both wired and wireless network virtualization, incorporating various academic references.