This document provides an overview of safeguarding policies and procedures for school staff. It discusses:
1) The roles and responsibilities of the school and staff in safeguarding children, including designating a safeguarding lead.
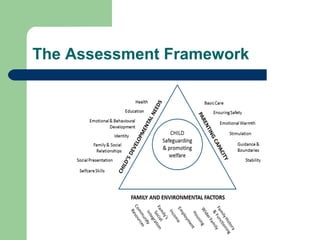
2) Defining safeguarding and the importance of maintaining a culture where children's safety and well-being are top priorities.
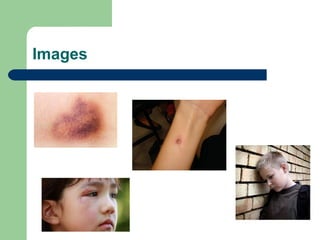
3) Educating staff on signs of abuse and neglect and the procedures to follow if they have concerns about a child, which includes reporting issues to the designated safeguarding lead.