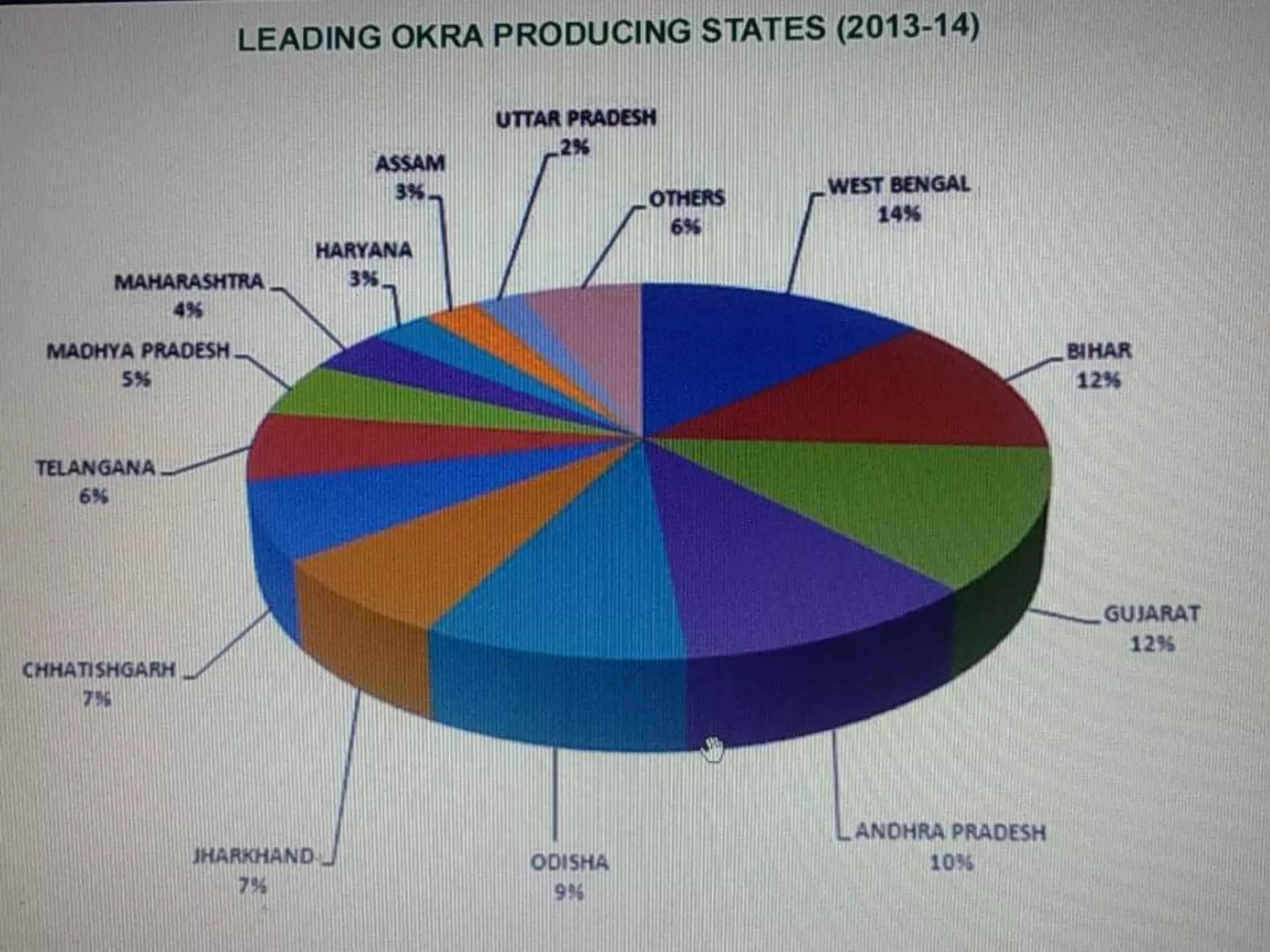
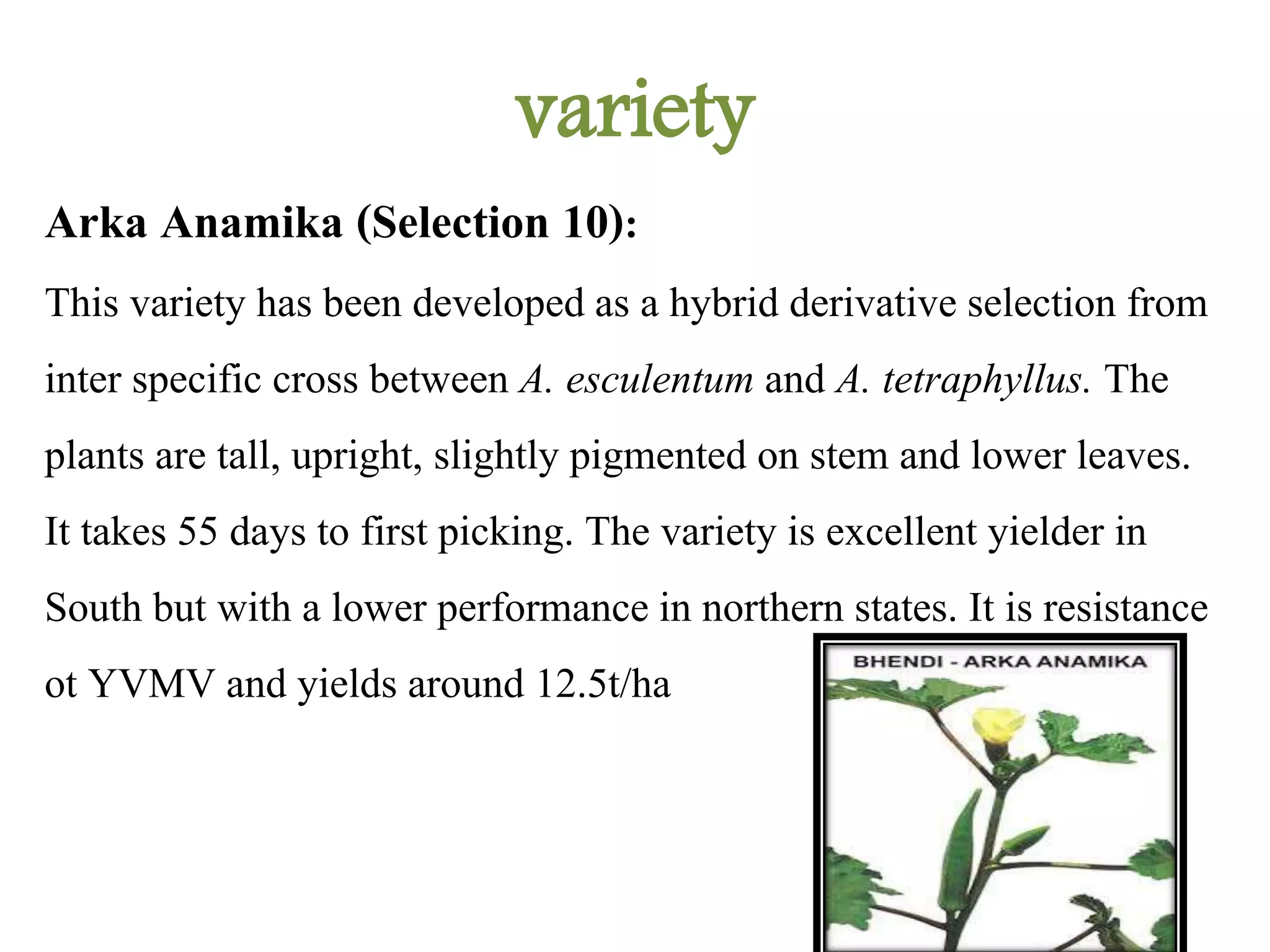
This document provides a presentation on okra summarizing its botanical details, production, varieties, cultivation practices and pests. It begins with the botanical name Abelmoschus esculents and family Malvaceae, noting it is commonly known as ladies finger. Varieties discussed include Arka Anamika, Arka Abhay, Parbhani Kranti and Pusa Sawani. The document outlines soil and climate preferences, and cultivation steps of seed treatment, spacing, irrigation, manures and pest management. Major pests include shoot and fruit borer, yellow vein mosaic virus, and leaf hopper.