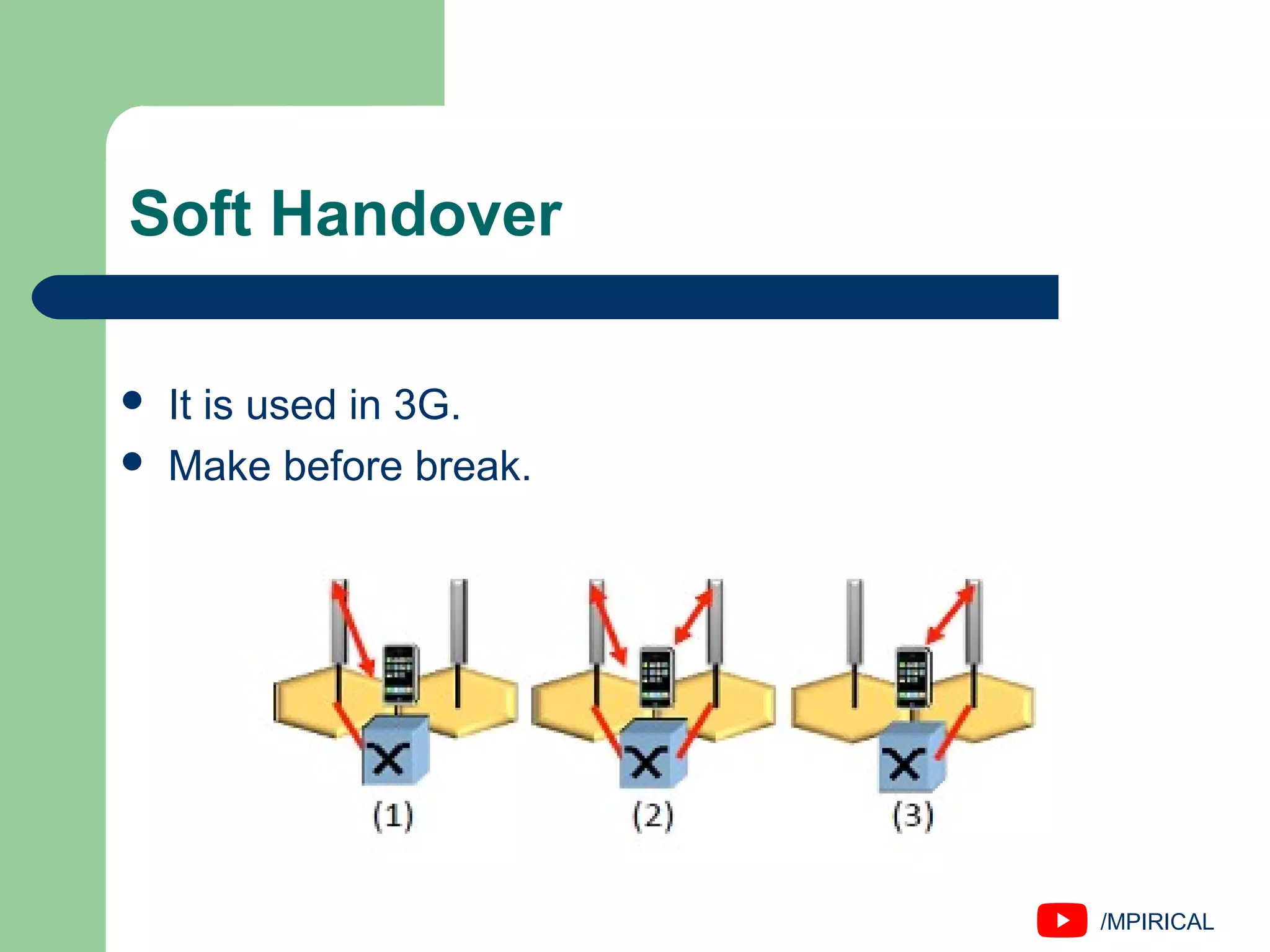
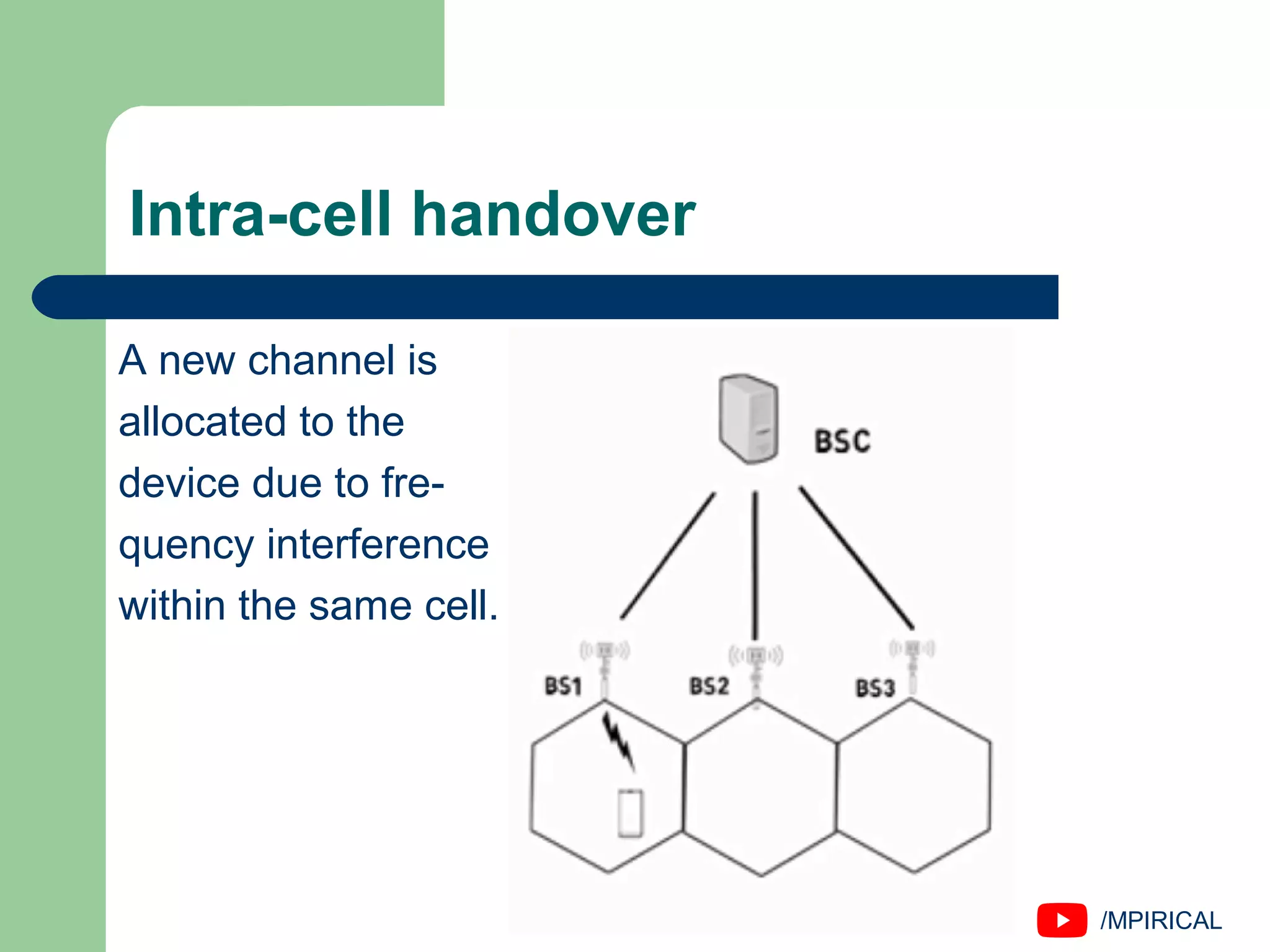
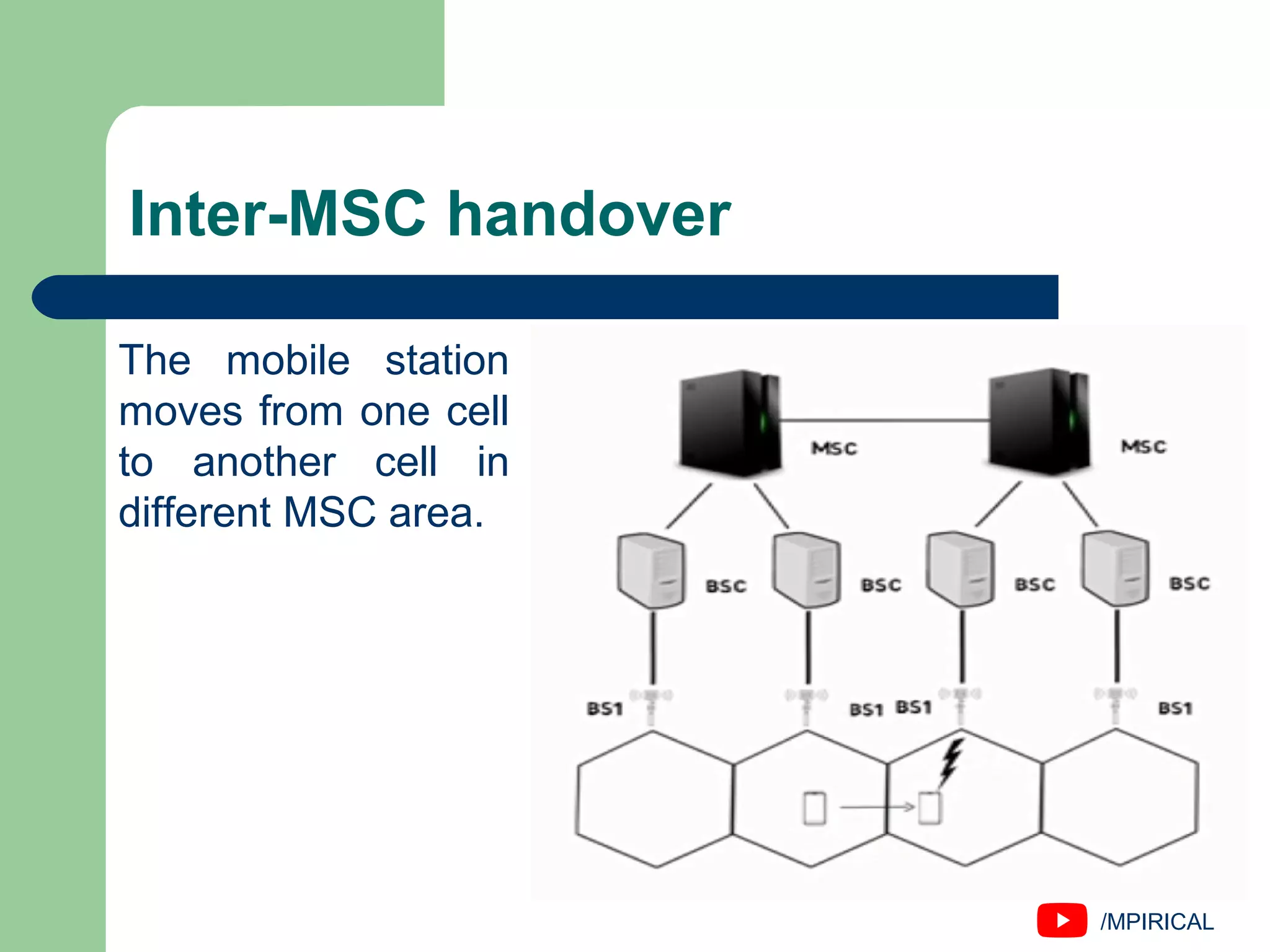
The document discusses handover management in wireless and mobile communications, defining handover as the transfer of communication control. It outlines types of handovers, including network-controlled, mobile-assisted, and mobile-controlled handoffs, along with their respective execution times and characteristics. It also distinguishes between hard and soft handovers and various intra-cell and inter-cell handovers.