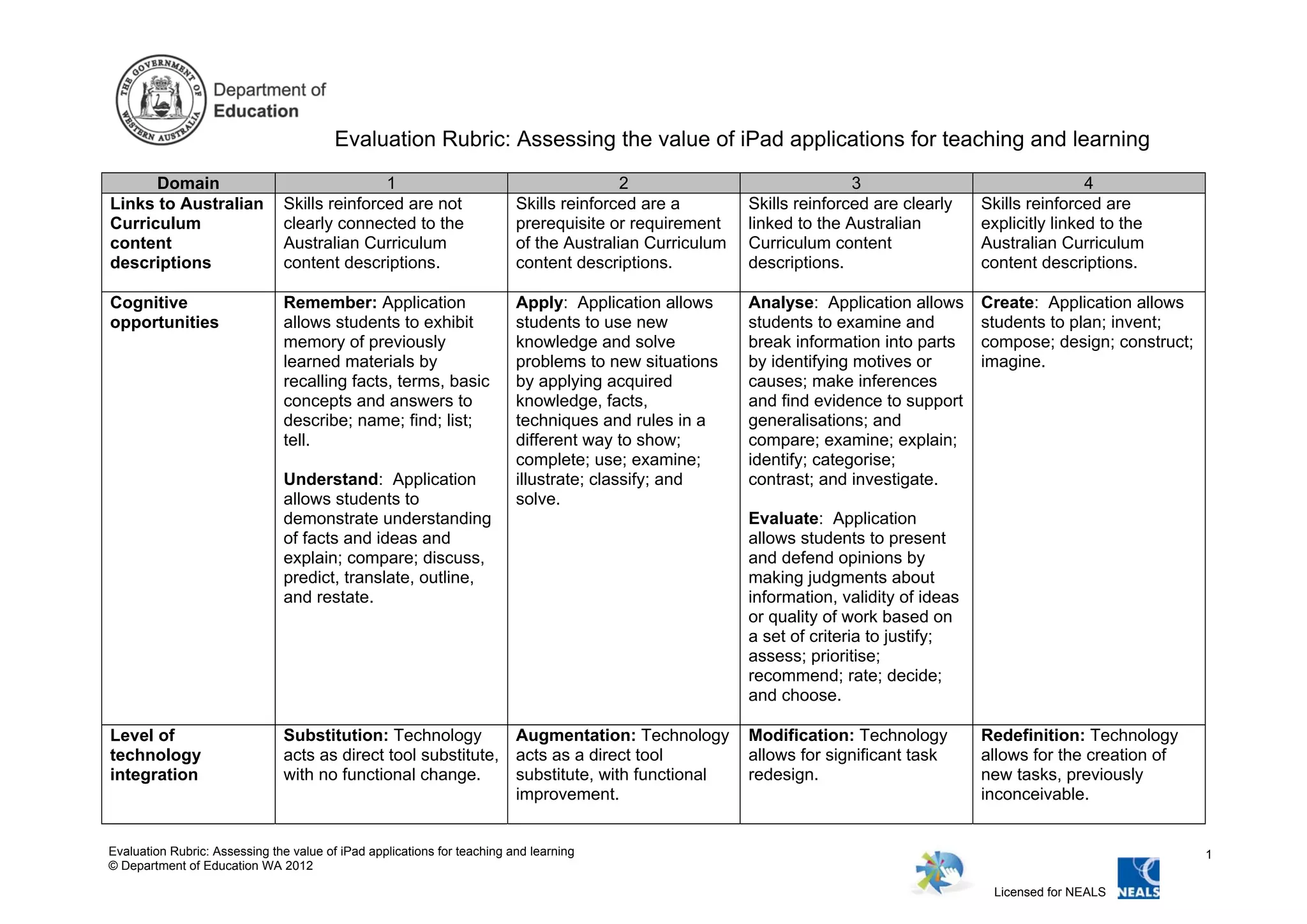
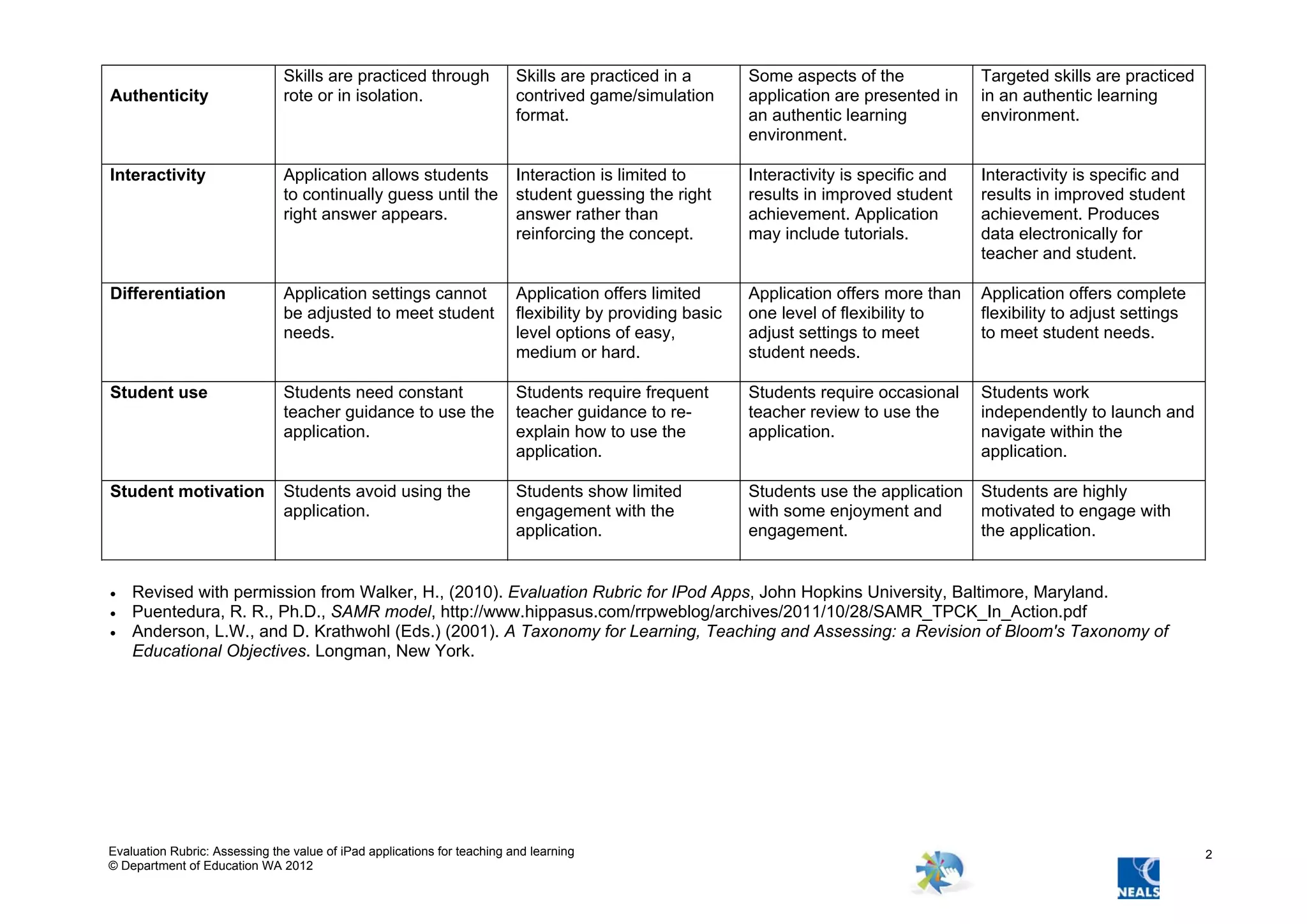
This document provides an evaluation rubric for assessing iPad applications for teaching and learning. The rubric evaluates applications across several domains from a 1 to 4 scale. The domains include links to curriculum, cognitive opportunities, level of technology integration, authenticity, interactivity, differentiation, student use, student motivation. For each domain, the rubric describes the characteristics of a rating of 1, 2, 3, or 4, with 4 being most desirable. For example, for cognitive opportunities, a rating of 1 involves remembering facts, while 4 involves creating, and for level of technology integration, 1 involves substitution of the technology for an existing tool, while 4 involves redefinition and new tasks not previously possible. The rubric provides a framework for