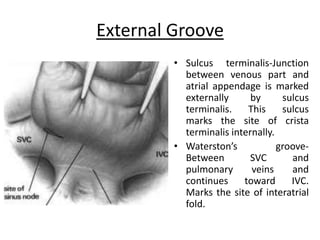
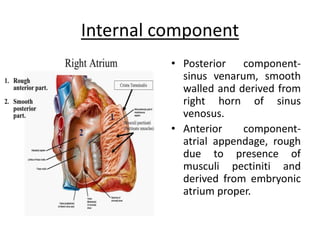
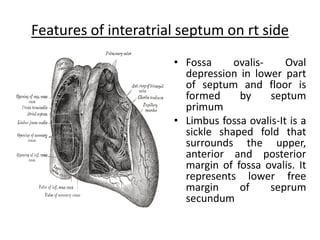
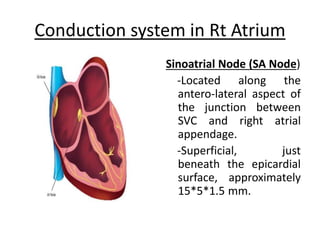
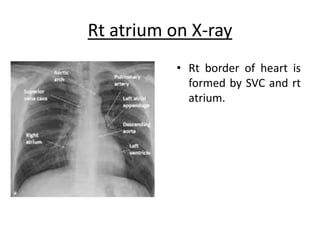
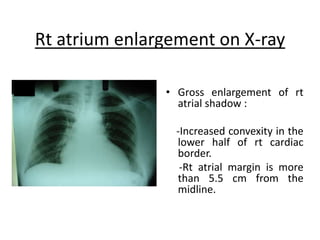
The right atrium receives systemic venous return from the superior vena cava and inferior vena cava. It has a triangular shape with a broad base and blunt appendage. The right atrium contains important structures like the crista terminalis, Eustachian valve, and Thebesian valve. The sinoatrial node is located near the junction of the superior vena cava and right atrial appendage. Right atrial enlargement can be caused by pulmonary hypertension, valvular diseases like tricuspid regurgitation, or atrial septal defects. The right atrium can be evaluated on chest x-rays, ECGs, and echocardiograms.