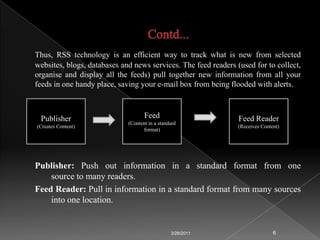
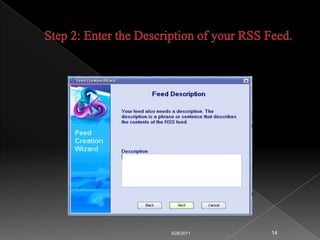
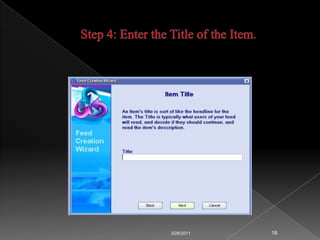
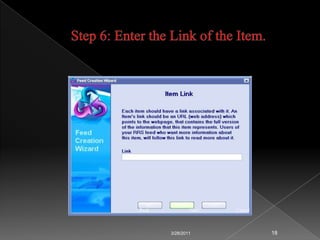
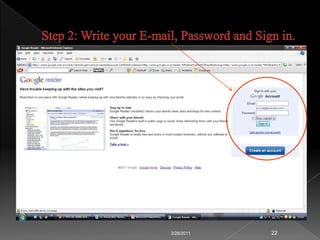
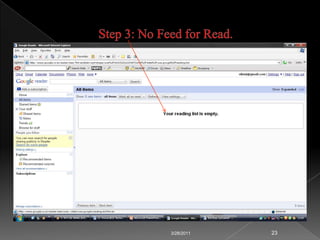
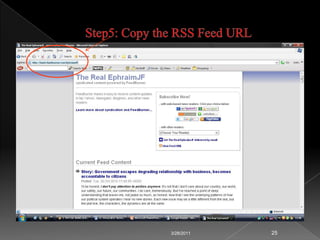
RSS technology allows publishers to syndicate updates from their websites in a standardized format that readers can subscribe to using feed readers. It simplifies finding and accessing up-to-date information from multiple sources. Libraries can use RSS to provide services like selective dissemination of information, current awareness, and bulletin boards by syndicating updates from databases, news, and other resources their users are interested in.