Routine lab tests provide important health information. Some common tests include:
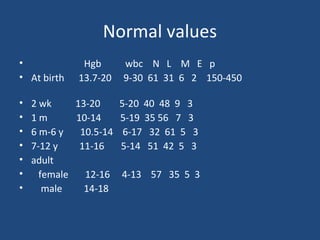
- A complete blood count evaluates red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. It screens for anemia and infection.
- Blood chemistries analyze chemical substances like electrolytes, kidney and liver enzymes, lipid profiles, and blood glucose. This provides insights into organ function.
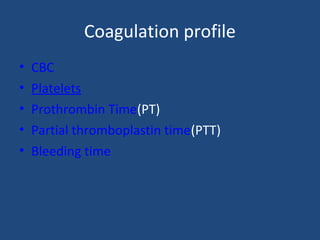
- Additional tests like coagulation profiles and hormonal assays evaluate risks of bleeding, metabolic conditions, and pregnancy.
Together, routine lab tests form a baseline of a person's health and can detect early signs of disease if values are outside normal ranges.