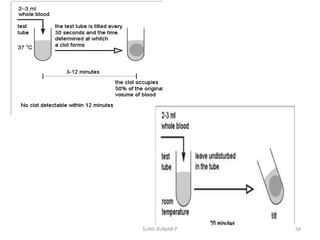
This document discusses various methods for measuring bleeding time and clotting time, which evaluate platelet function and coagulation, respectively. It describes Ivy's method for measuring bleeding time, which involves making three punctures on the forearm and timing how long it takes for bleeding to stop. The standard template method is also discussed. For clotting time, it covers the venepuncture method using two syringes and timing clot formation in a test tube, as well as the capillary method involving puncturing the skin and timing fibrin formation in a capillary tube. Normal ranges and clinical significance of prolonged or shortened times are provided.