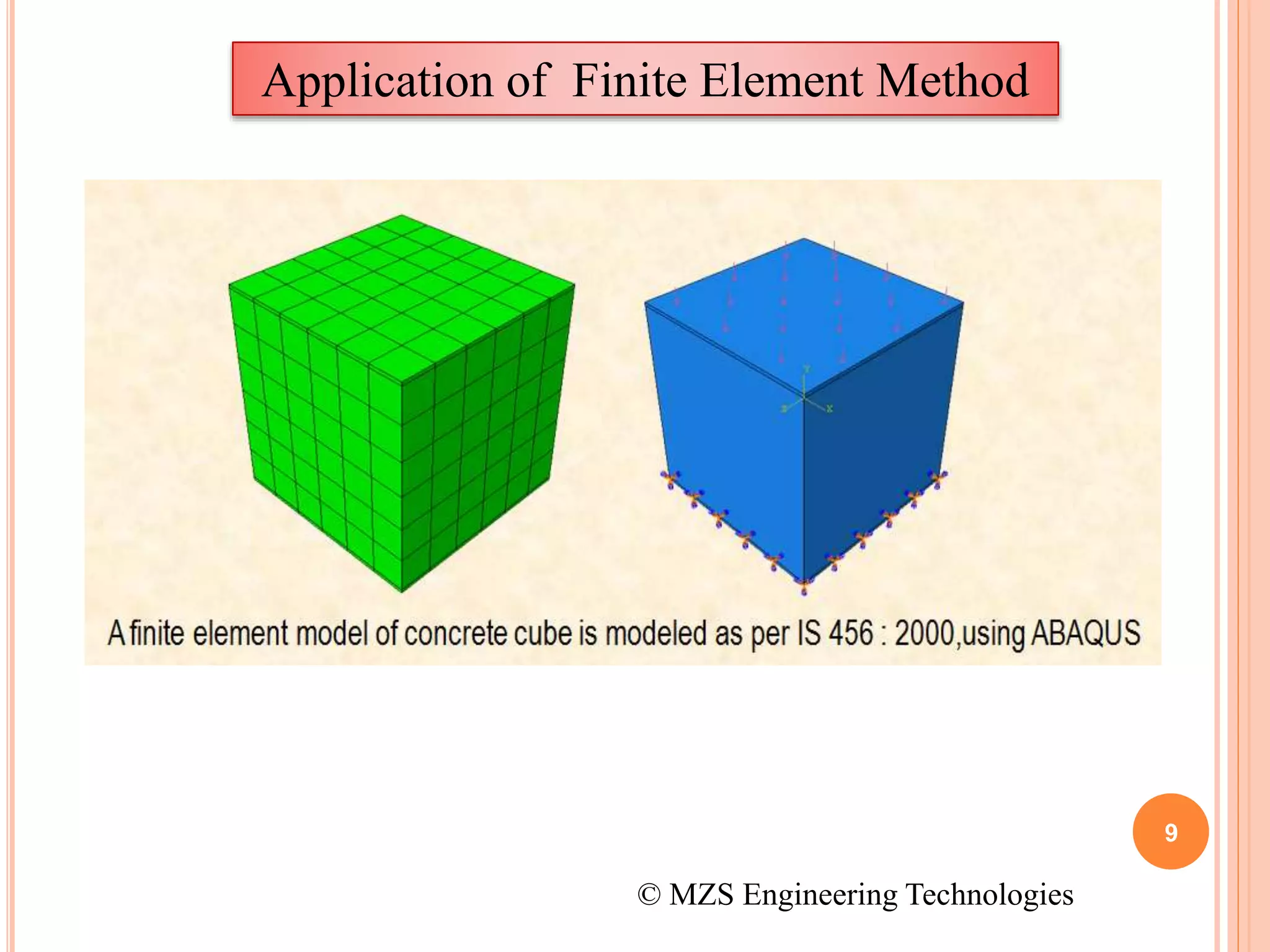
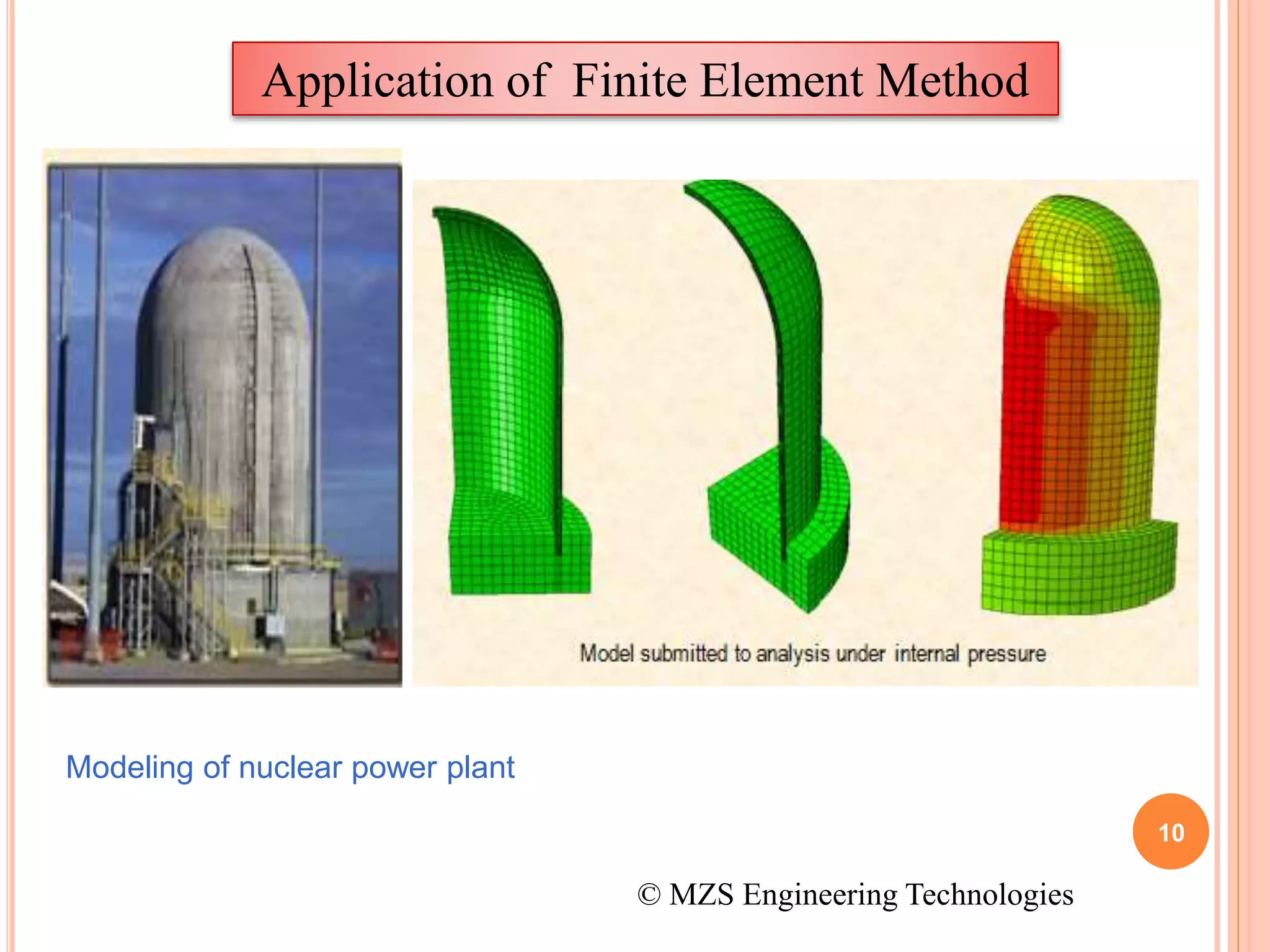
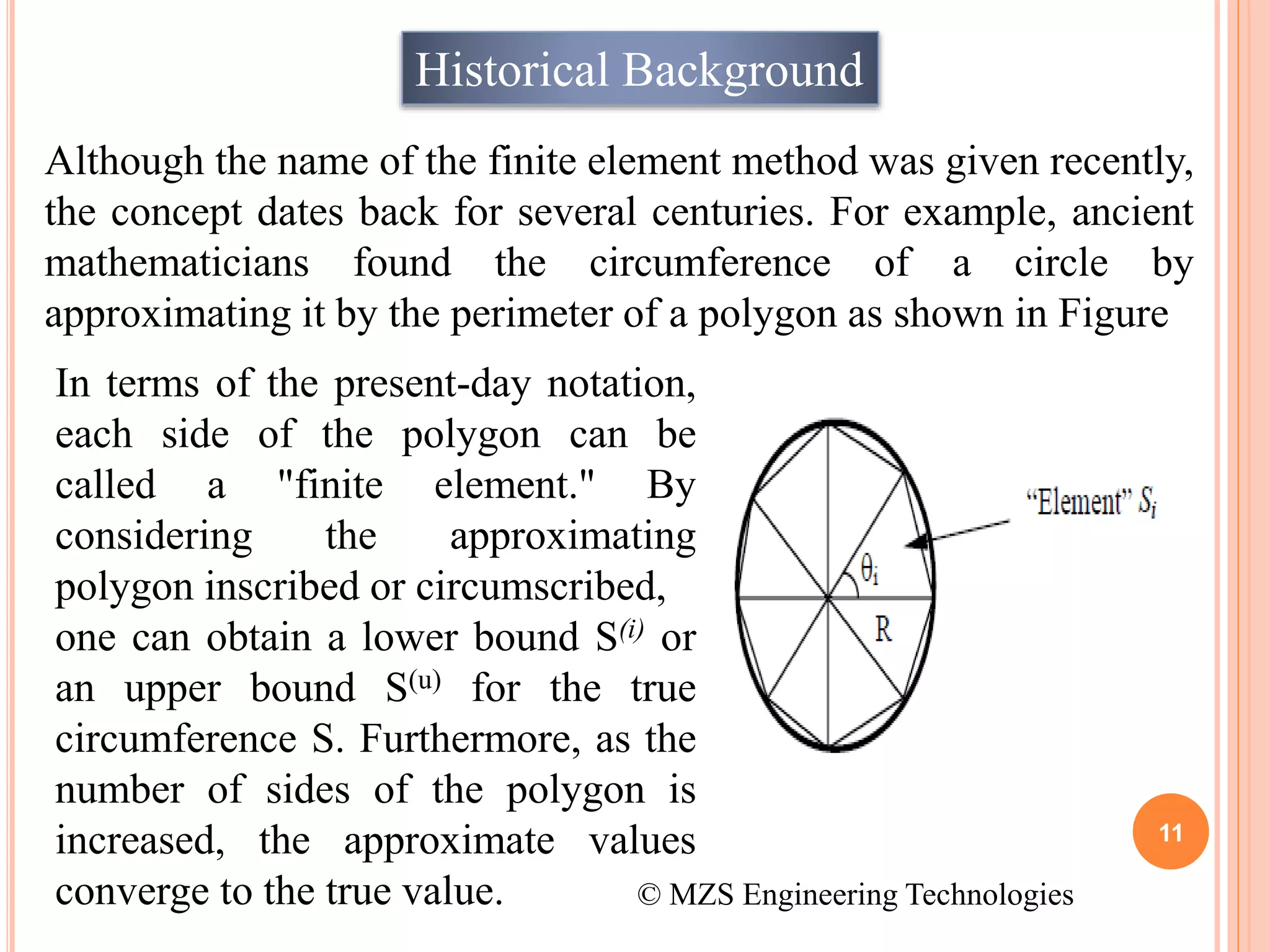
The document provides an introduction to the finite element method (FEM). It discusses that FEM is a numerical technique used to find approximate solutions to partial differential equations. It involves dividing a complex structure into smaller, simpler parts called finite elements and solving sets of algebraic equations. Commercial FEM software programs allow users to analyze complex engineering problems without an in-depth knowledge of mathematics. The document gives examples of how FEM can be used to model different structures and its applications in fields like mechanics, thermal analysis, and biomechanics.