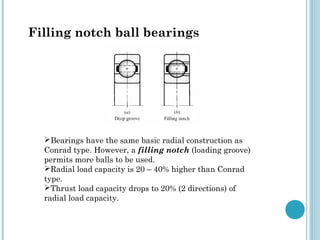
Rolling element bearings transmit loads through rolling contact and provide lower coefficients of friction than sliding contact bearings. They are composed of an inner race, outer race, rolling elements (balls or rollers), and a cage. Ball bearings are further classified as deep groove, angular contact, or filled notch types. Roller bearings use cylindrical or tapered rollers and have higher load capacity than ball bearings. Bearing life is rated based on the number of revolutions or hours it can operate before spalling or pitting failure occurs, with an L10 life rating meaning 10% of tested bearings will fail by that point.