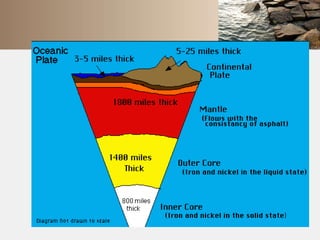
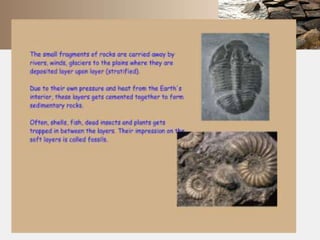
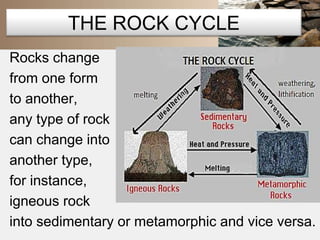
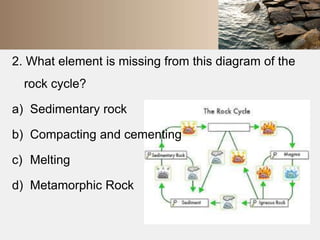
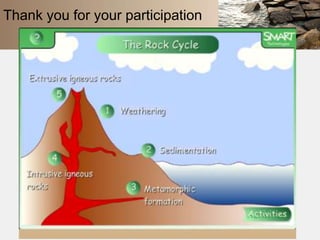
Rocks are naturally occurring mixtures of minerals that are classified based on their formation and composition. Rocks change over time through the rock cycle. There are three main types of rocks: igneous rocks formed by cooling magma, sedimentary rocks formed from compacted sediments, and metamorphic rocks formed by changes to existing rocks through heat and pressure. Rocks can change from one type to another through the rock cycle.