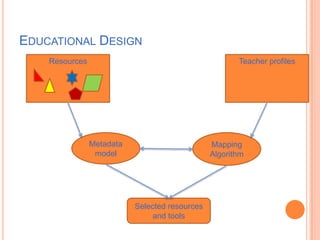
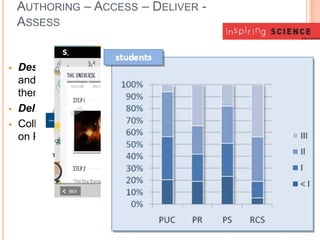
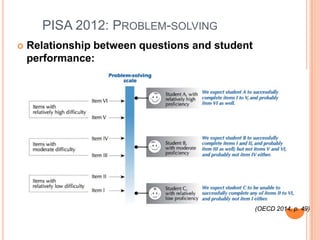
The document proposes the creation of the European Science Education Academy (ESEA) to promote best practices in science education across Europe. The goals of ESEA are to 1) influence science teaching approaches, 2) document innovation in teacher professional development, 3) create an accessible repository of best practices, and 4) provide policy advice. ESEA will develop guidelines, identify resources, support communities of practice, and disseminate information to stakeholders including teachers, policymakers, and educational organizations. Initial funding from PATHWAY and other projects will support developing the conceptual framework, repository, and teacher training programs to improve science education.