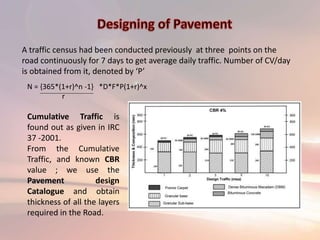
The document summarizes the process of widening and strengthening an existing road from 3m to 7m wide and describes the quality control tests performed on materials. It involves excavating the existing crust, laying new granular sub-base and wet mix macadam layers which are compacted. A bituminous surface layer is then applied. Culverts and bridges are also constructed along the road. Pile foundations are installed for the new bridge by driving casings into the ground and filling with concrete.