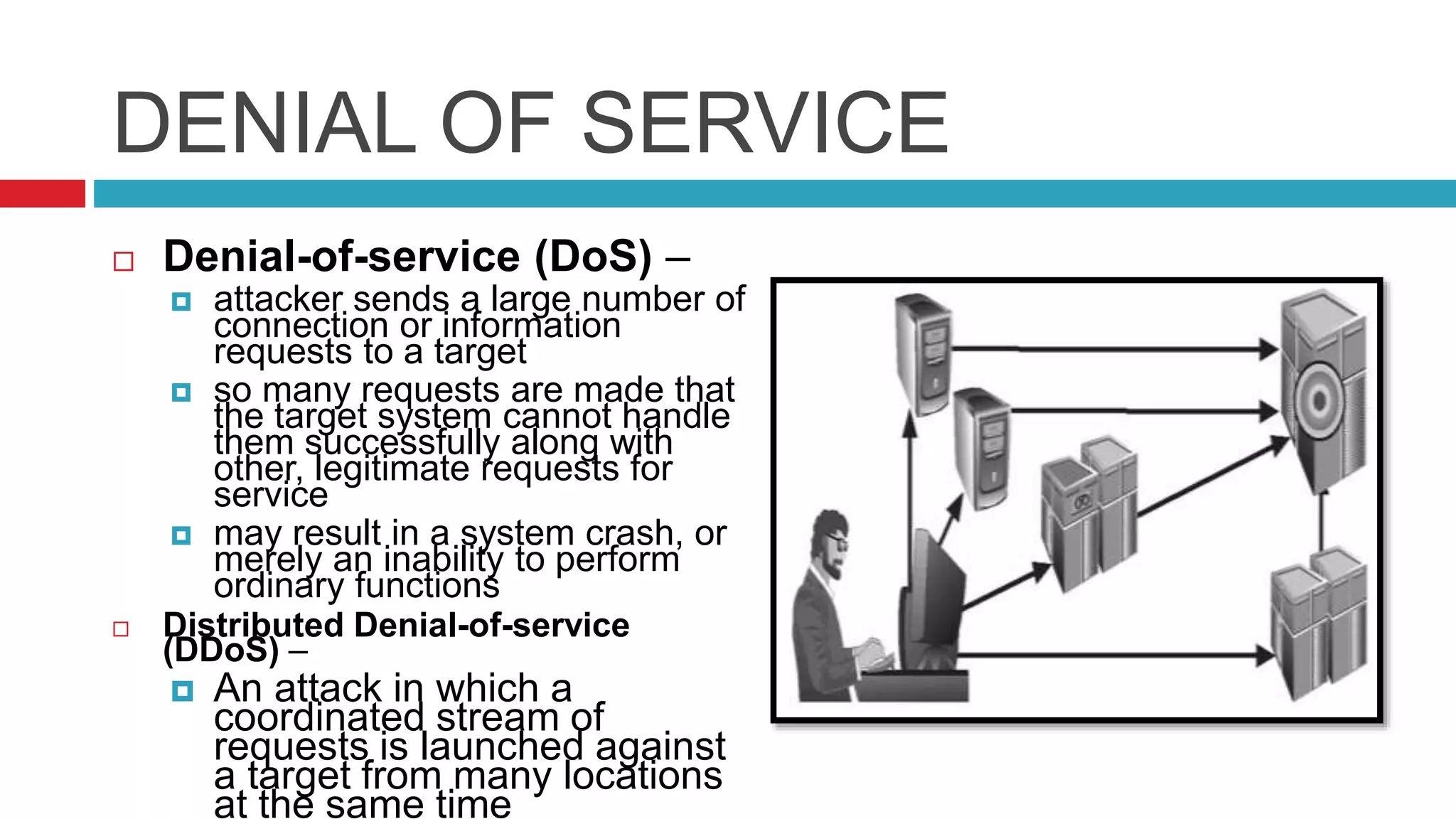
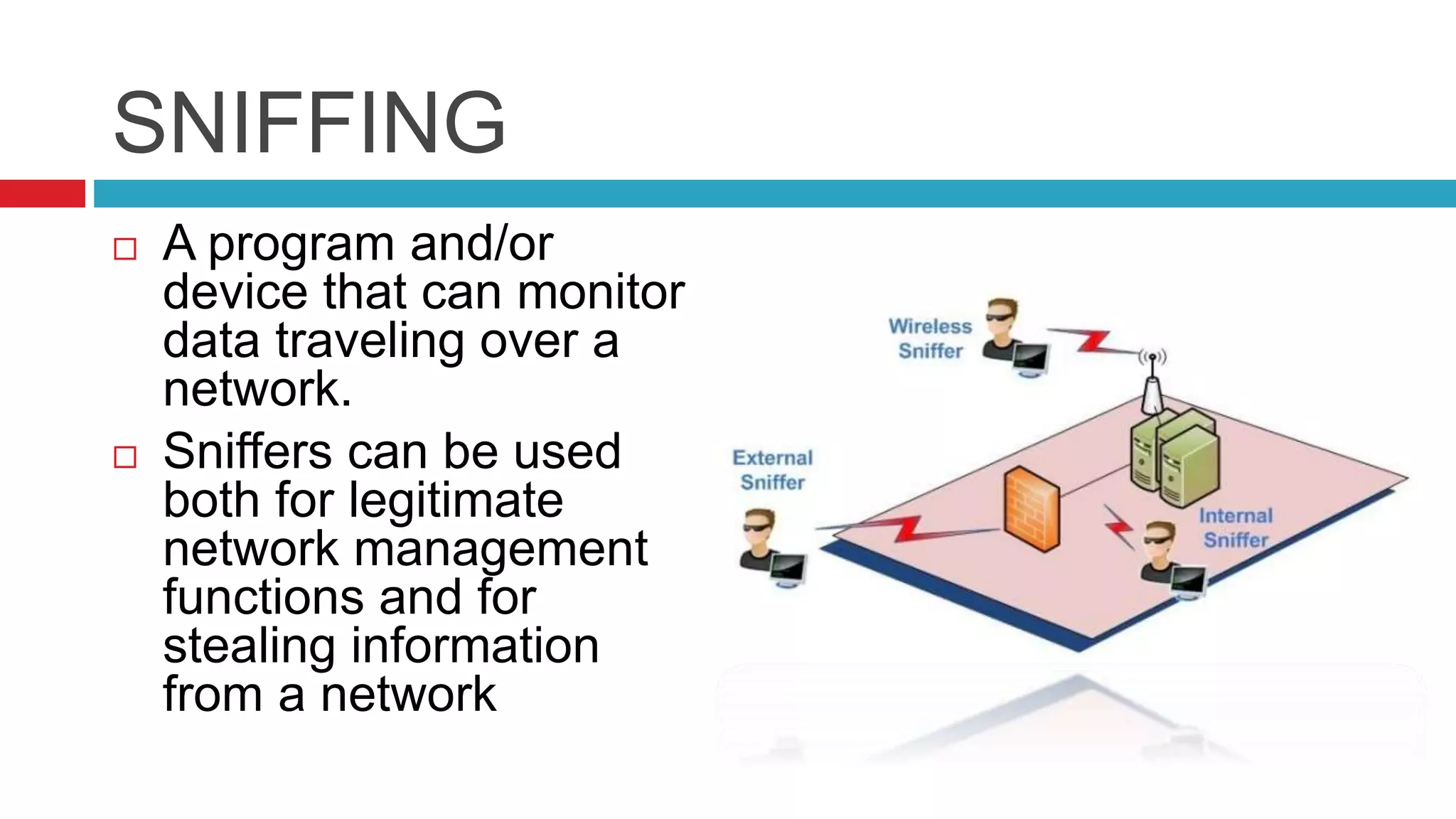
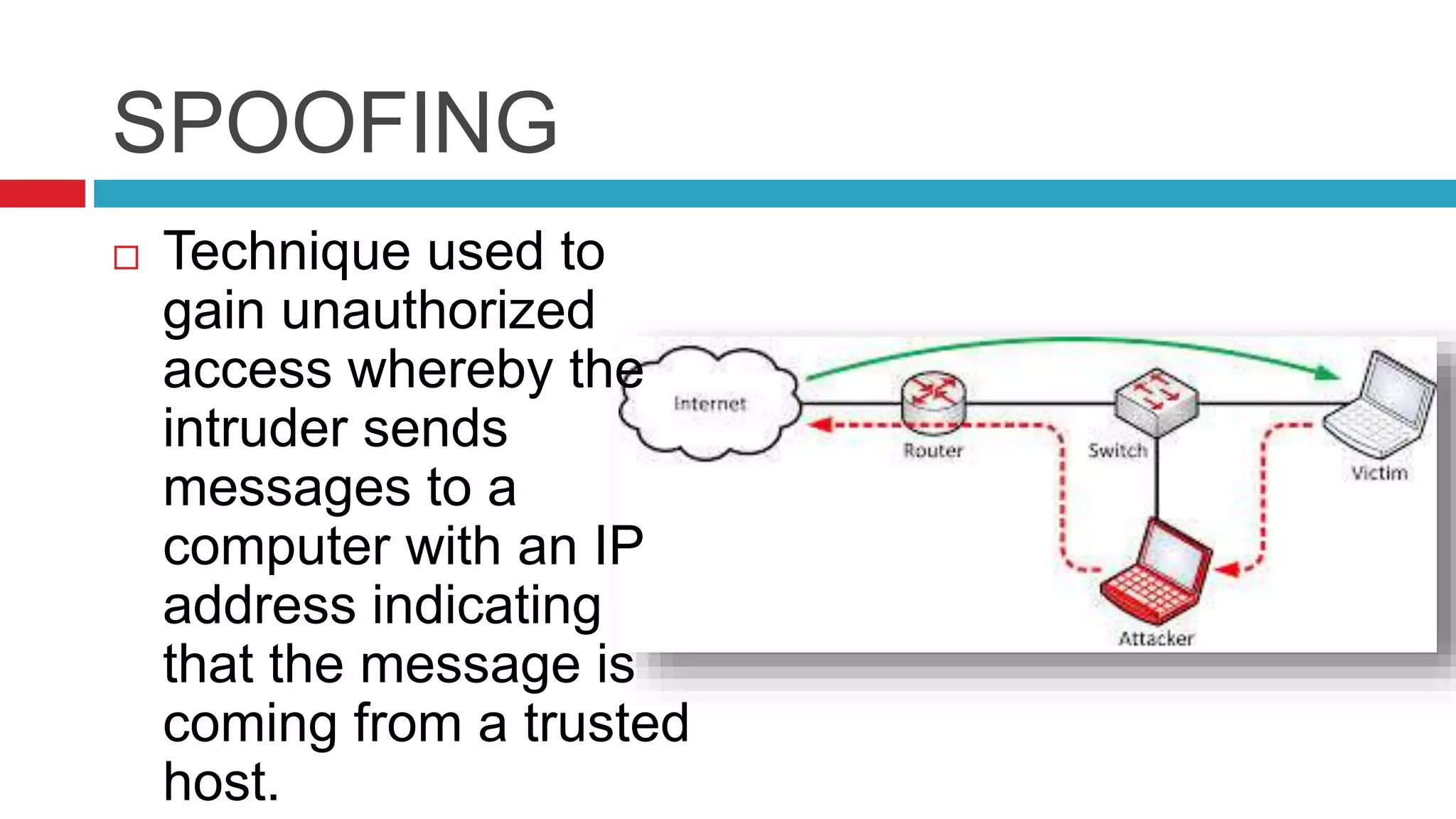
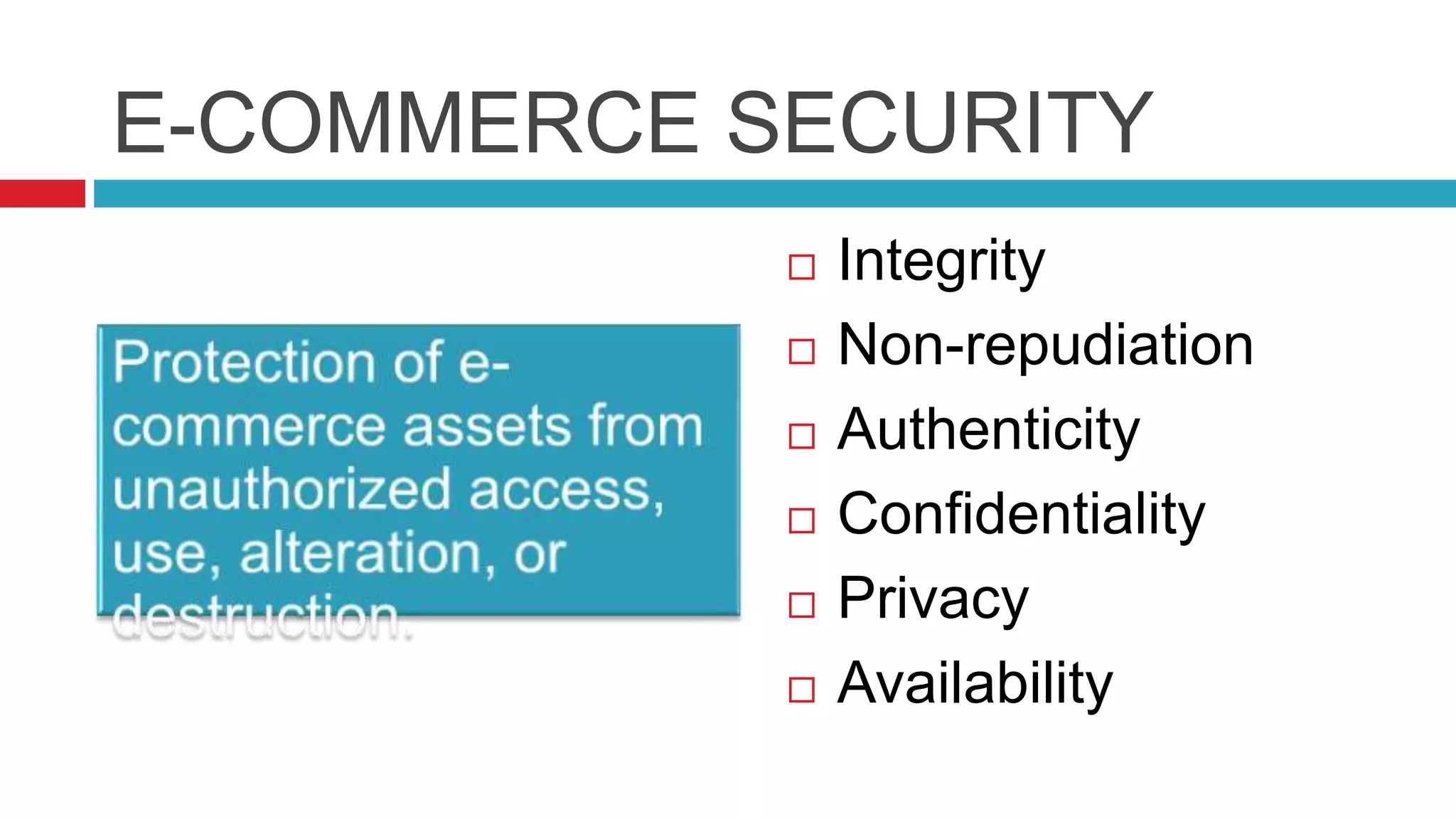
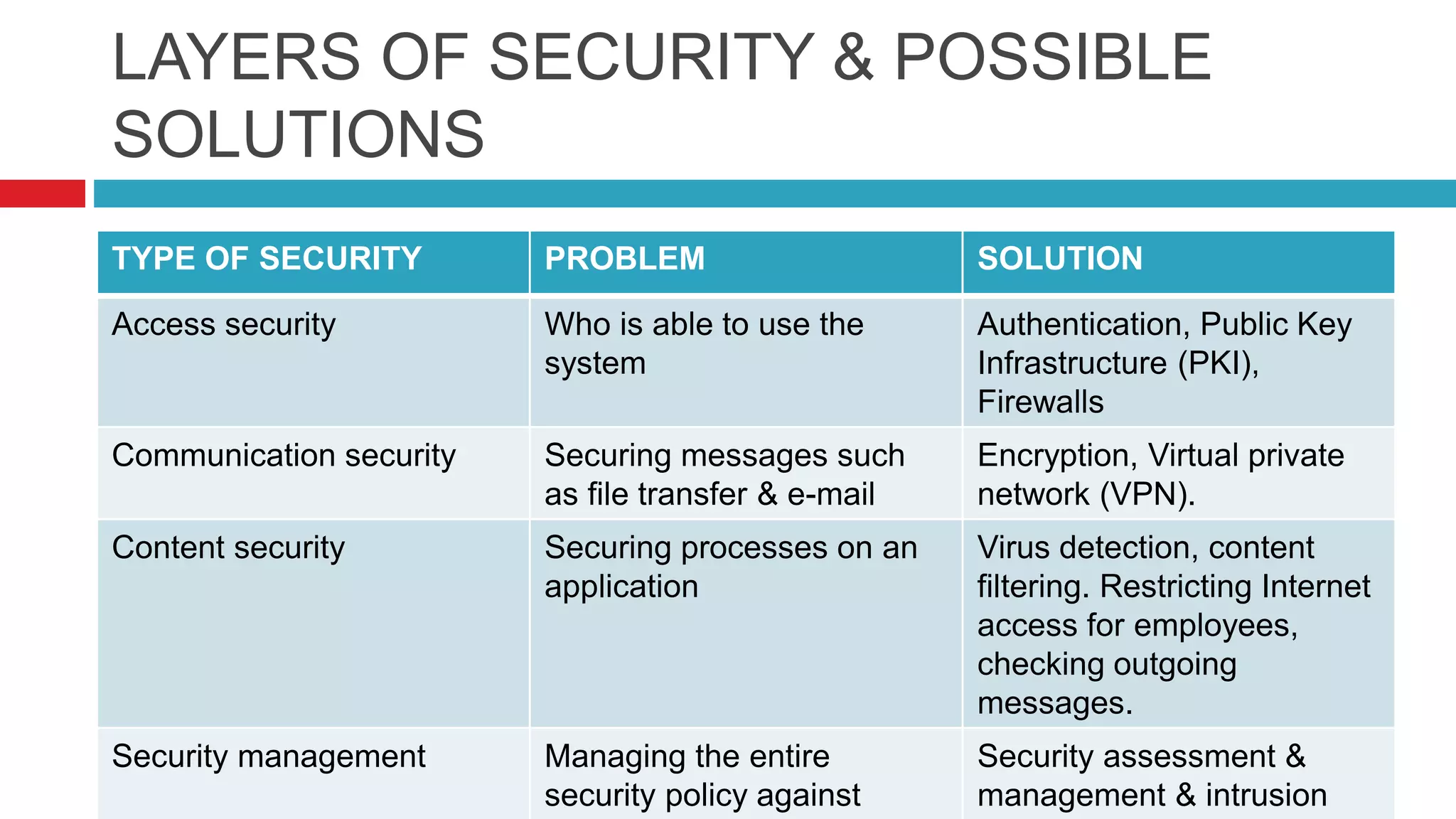
This document discusses security risks and considerations for e-commerce. It outlines several key security aspects including privacy, integrity, authentication, non-repudiation, availability, and confidentiality. It then describes common security threats like viruses, Trojan horses, worms, denial of service attacks, sniffing, spoofing, intellectual property theft, and hacking. Finally, it discusses some measures to secure e-commerce like digital certificates, encryption, firewalls, and antivirus software. The goal is to protect against threats while ensuring the privacy, integrity, authentication, and availability of e-commerce systems and transactions.