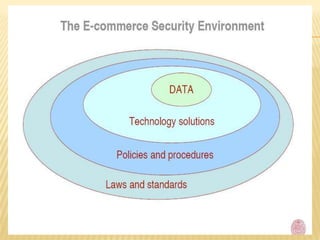
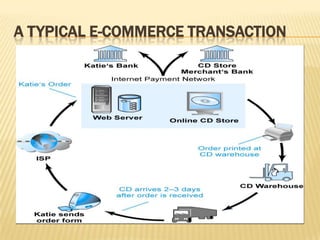
The document discusses security threats in e-commerce, including various types of malicious code, unwanted programs, phishing and identity theft, hacking and cybervandalism, credit card fraud, spoofing and spam websites, denial of service attacks, and other threats such as sniffing and insider jobs. It also outlines some technology solutions for protecting internet communications through encryption, securing communication channels, protecting networks with firewalls, and protecting servers and clients.