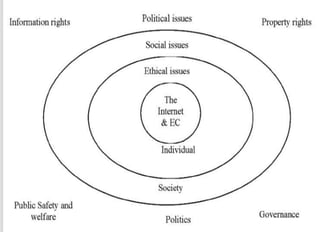
This document discusses several legal and ethical issues related to e-commerce, including privacy and information rights, property rights, governance issues, and public safety concerns. It outlines India's Information Technology Act of 2000, which provides the legal framework for e-commerce and addresses cybercrime. Specific issues covered include security threats to e-commerce like hacking and viruses; legal issues involving incorporation, trademarks, and transactions; and the regulation of internet gambling. Ethical concepts around responsibility, accountability, and analyzing dilemmas are also examined.