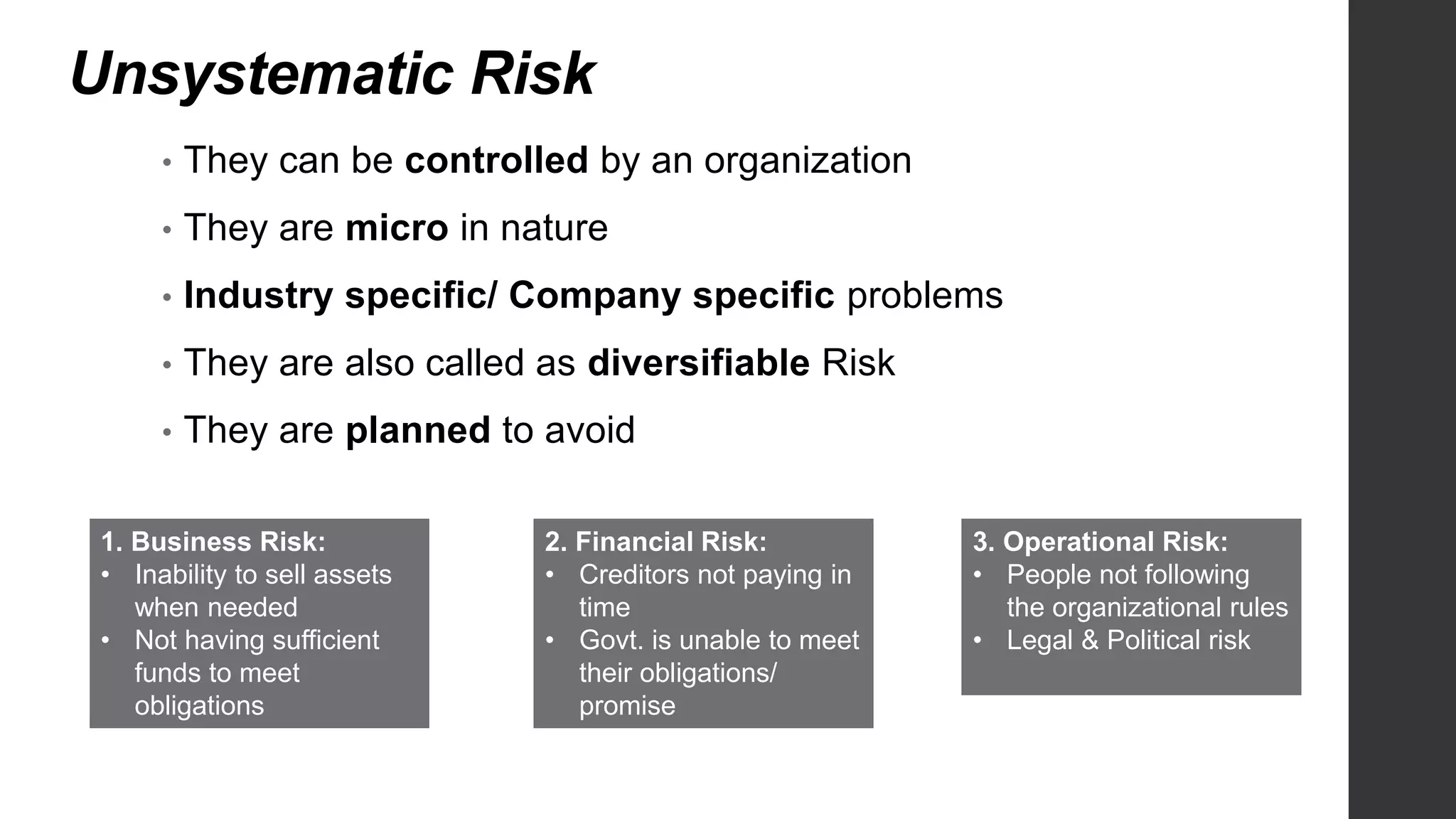
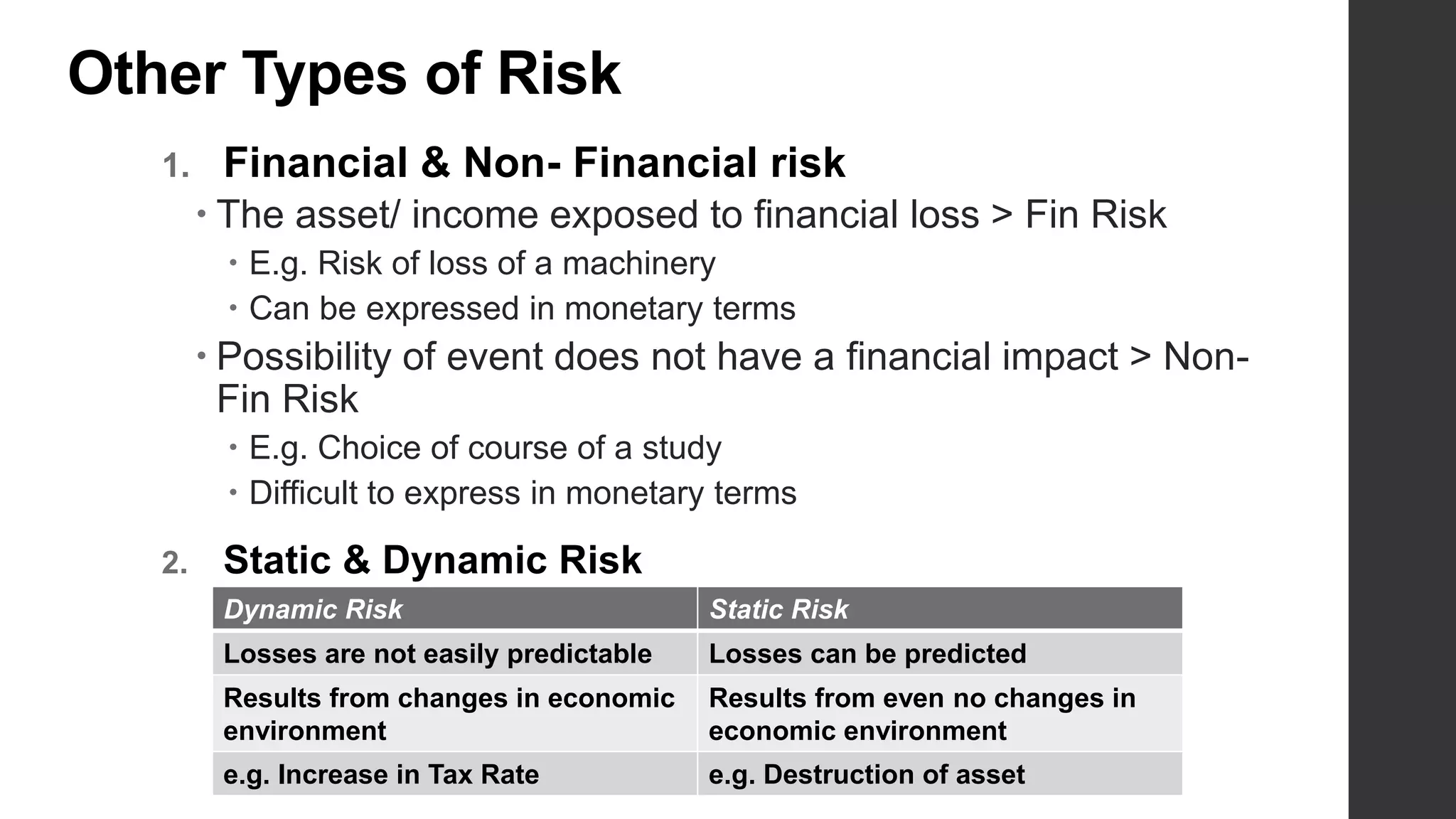
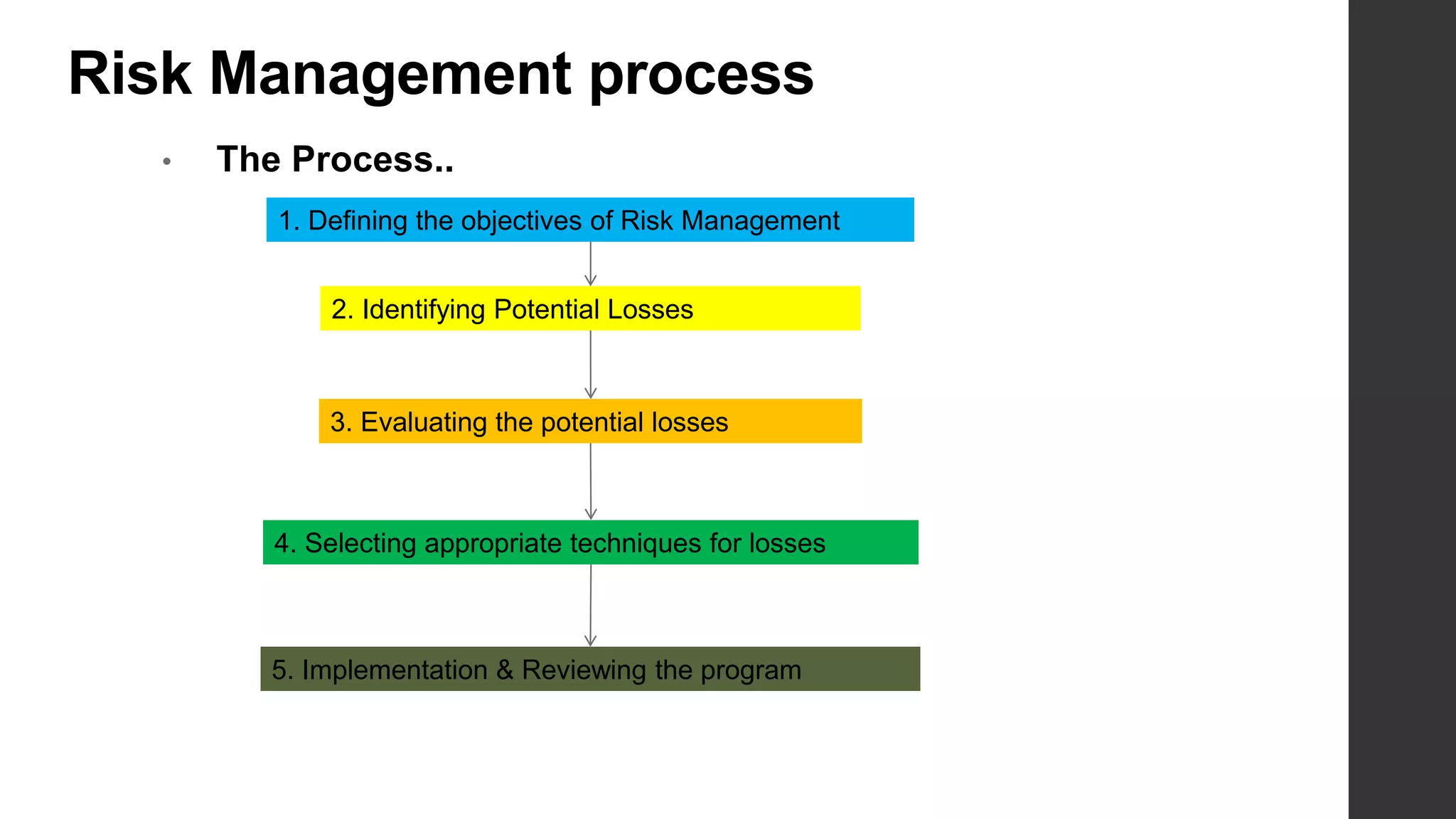
This document provides an introduction to risk management. It defines risk and uncertainty, and discusses the types of risk including systematic, unsystematic, financial and non-financial risk. The objectives of risk management are to identify risks, reduce scandals, ensure data security, identify opportunities, and eliminate hindrances for long-term organizational objectives. Risks can be identified through sources like competitors, employees, customers, technologies, laws and regulations. The key steps in the risk management process are defining objectives, identifying potential losses, evaluating losses, selecting risk treatment techniques, and implementing and reviewing the risk management program.