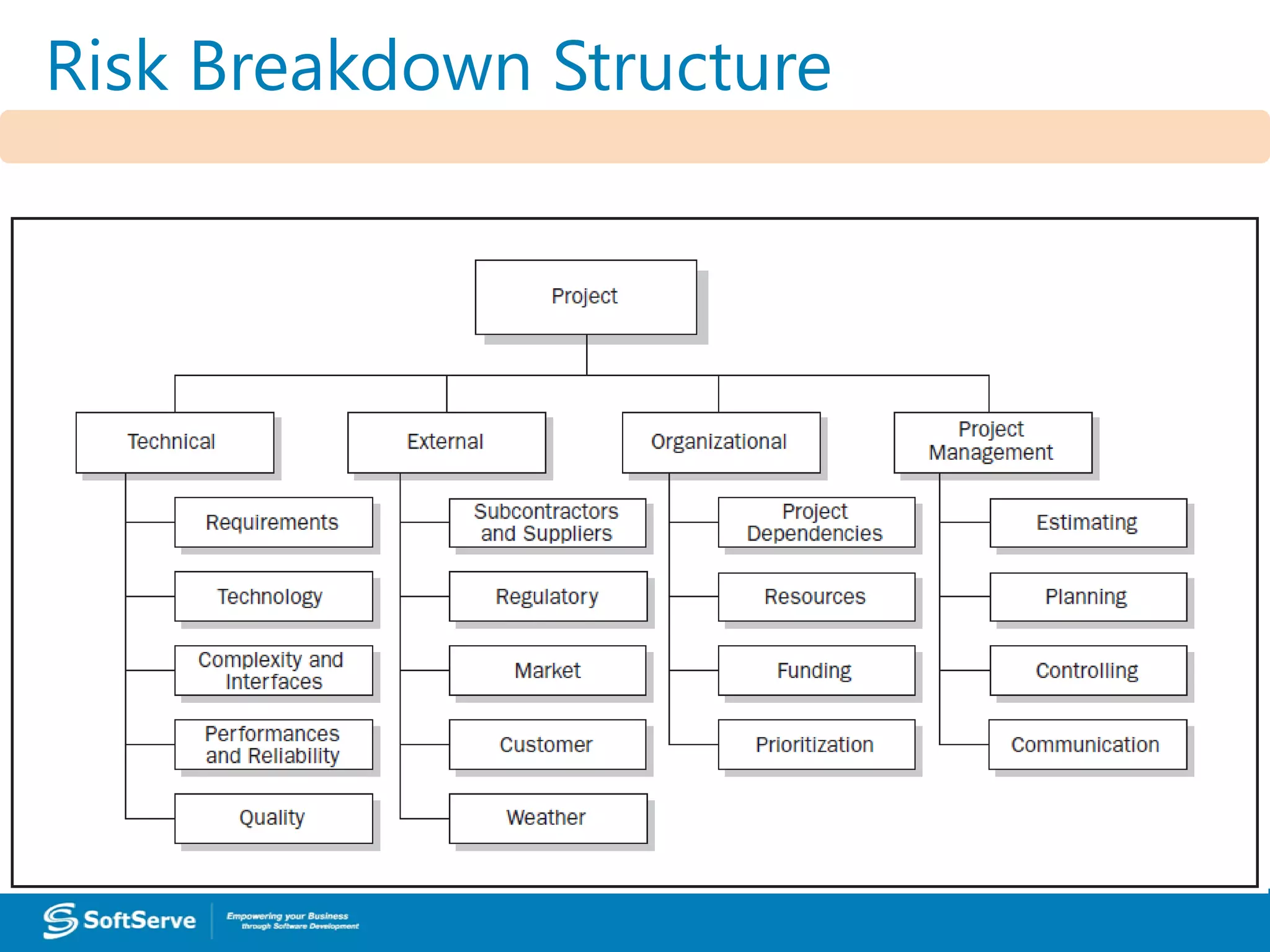
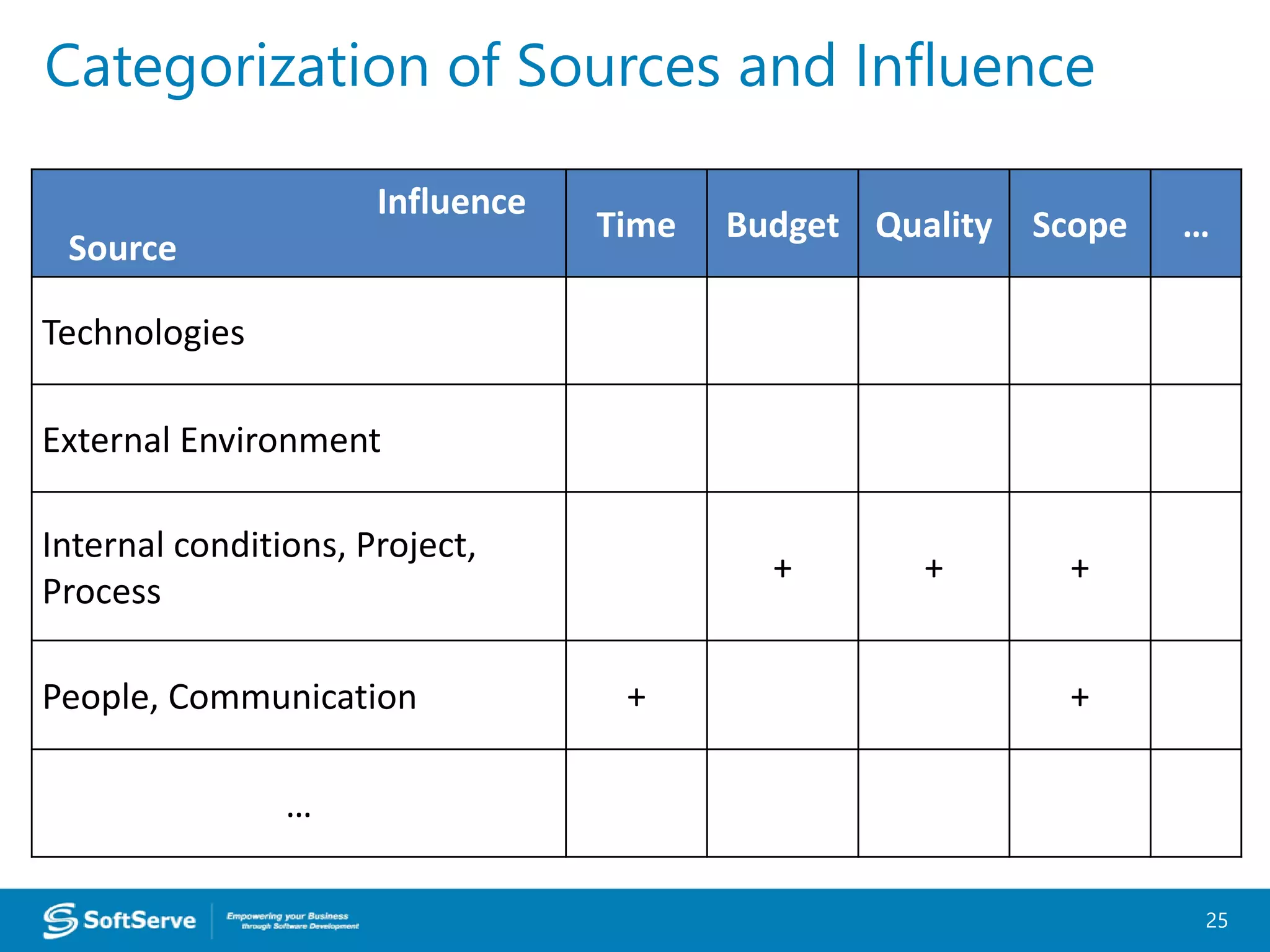
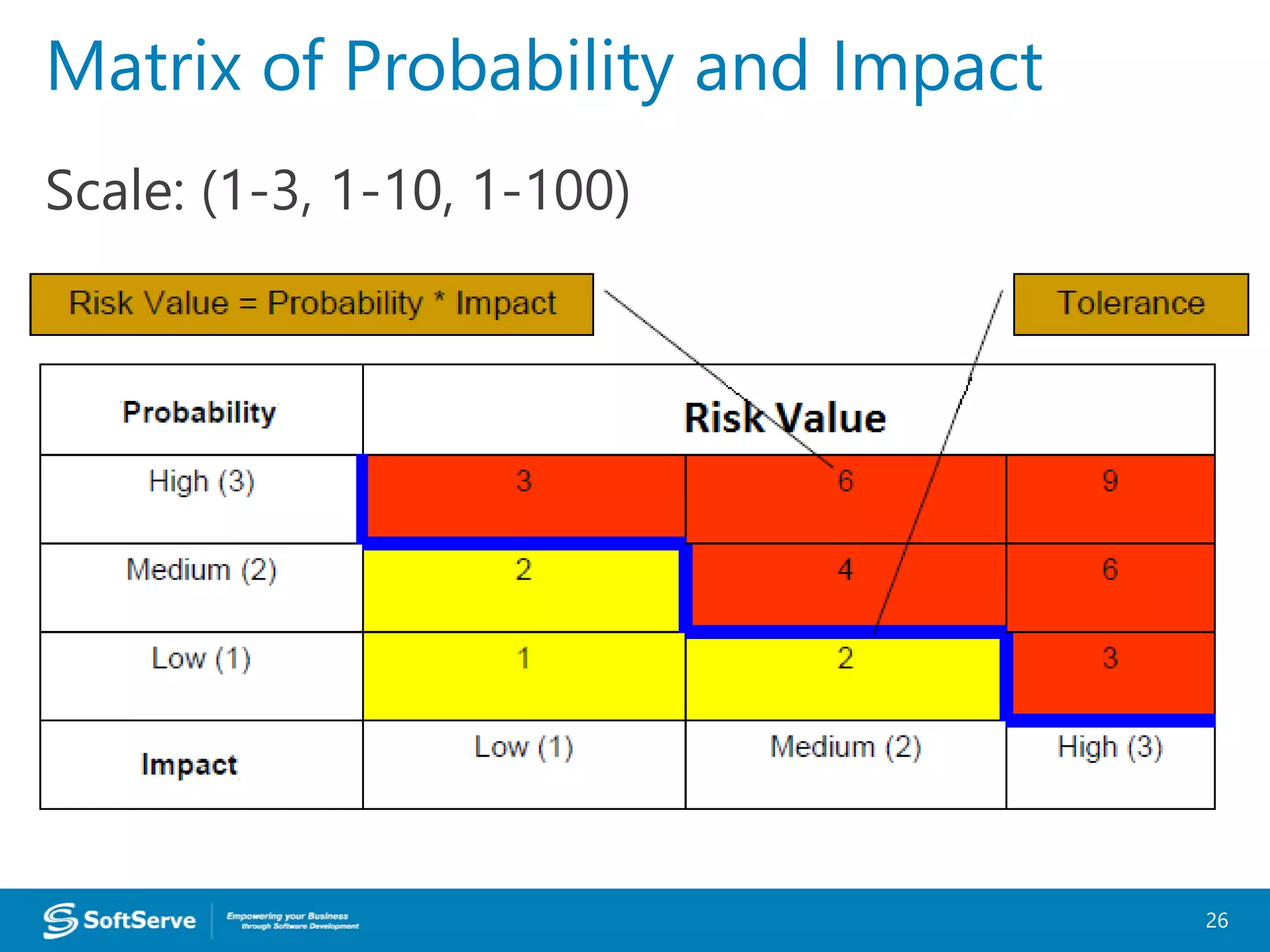
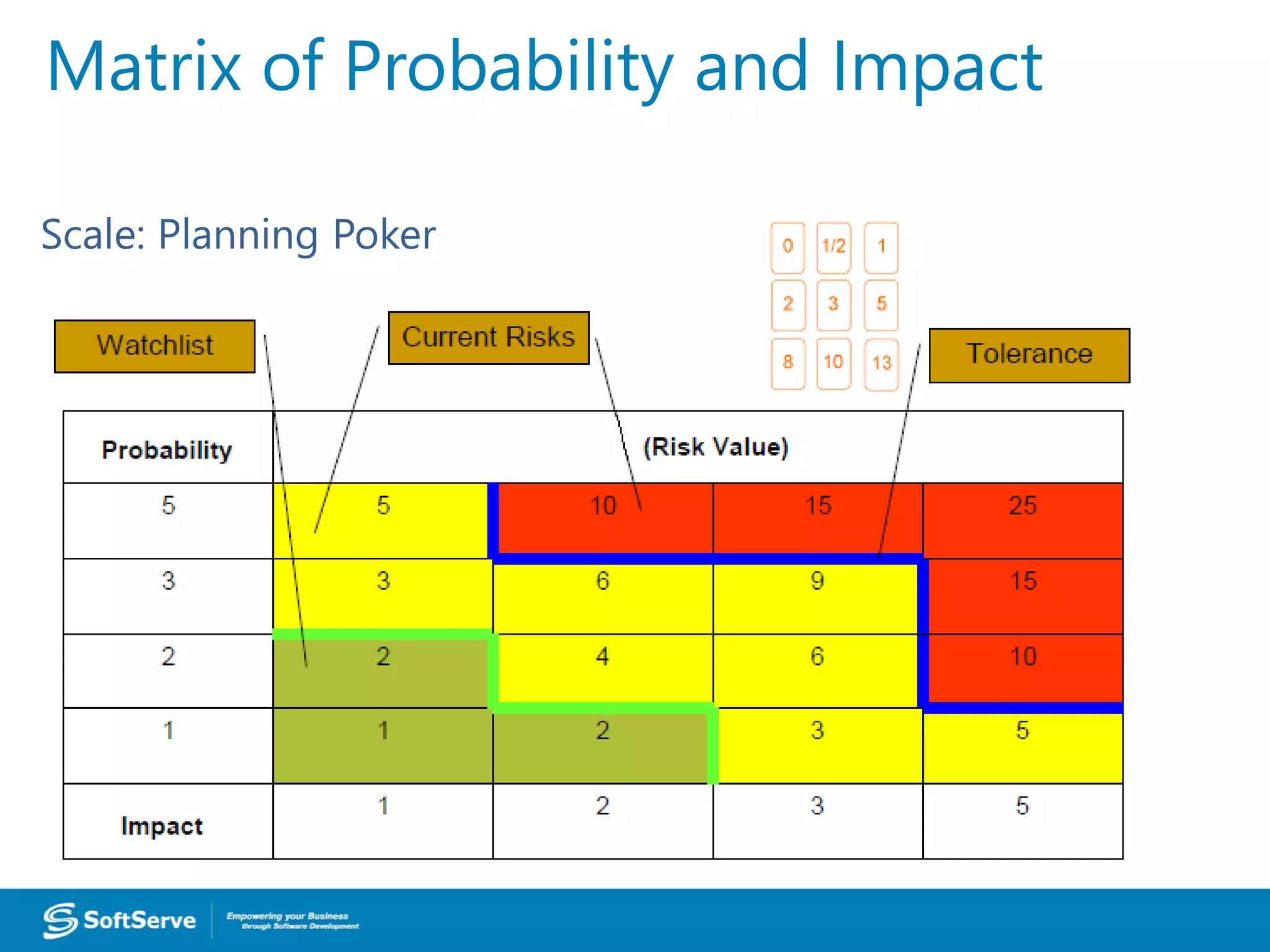
1. Requirements are only 50% defined, posing a risk of unclear or changing requirements which could lead to delays or scope issues.
2. Critical database performance is a risk area that must meet strict acceptance criteria.
3. The project team is missing 5 key resources which could cause delays if tasks take longer than expected to complete.
4. The database architect is only available 60-70% of the time due to another project assignment, posing a risk to timely database design and implementation.
5. Communication risks exist due to the client's main expert Jar Jar Binks not regularly using email and having a strong non-