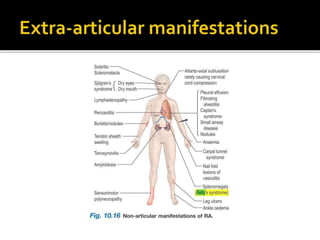
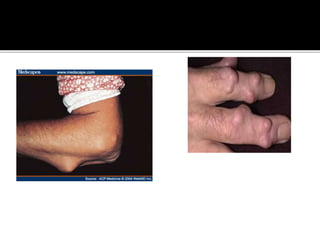
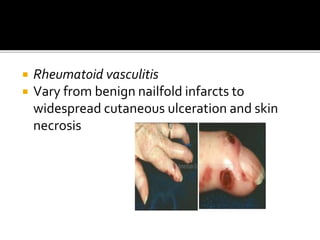
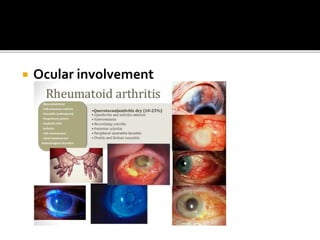
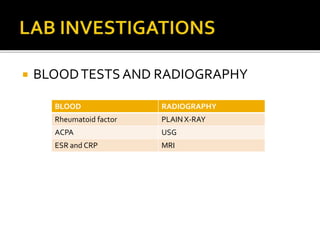
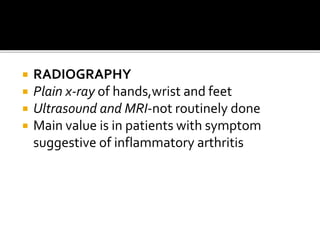
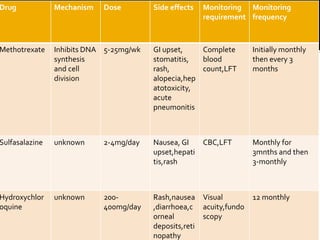
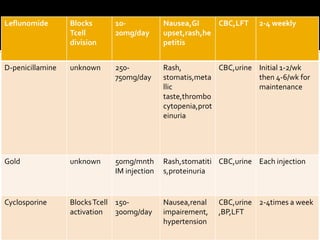
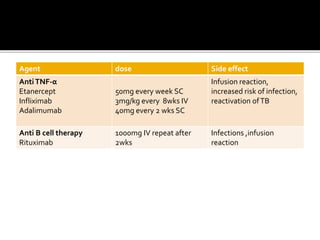
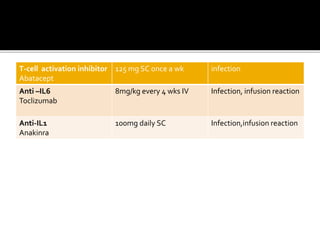
This document summarizes the various systemic manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis. It discusses how rheumatoid nodules can form on areas of friction and rheumatoid vasculitis can cause skin ulceration and necrosis. It also outlines potential involvement of major organ systems like the eyes, heart, lungs, blood, muscles and bones. Key diagnostic tests like rheumatoid factor, anti-CCP antibodies and radiography are mentioned. Common disease-modifying drugs for treatment as well as general measures and surgery are briefly covered.