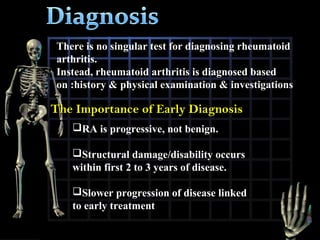
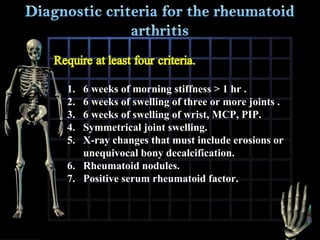
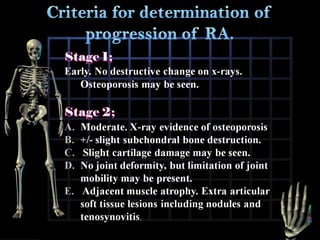
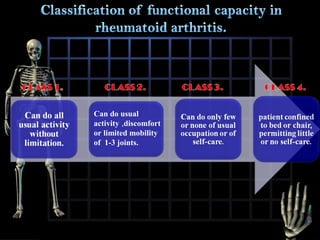
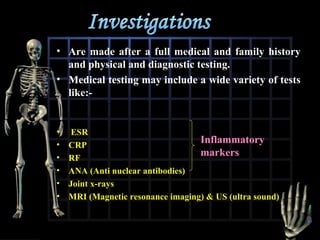
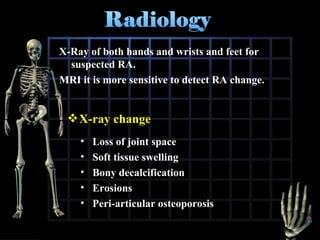
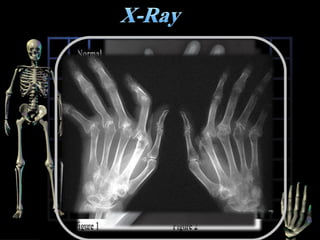
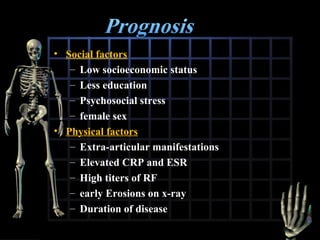
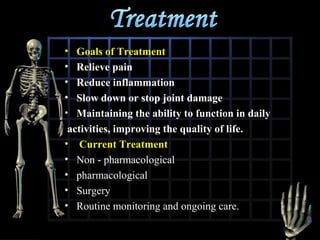
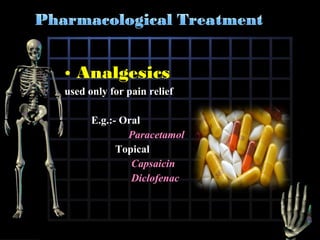
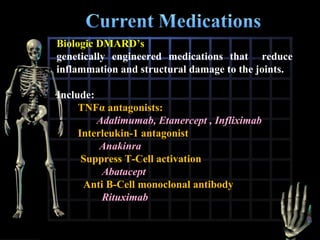
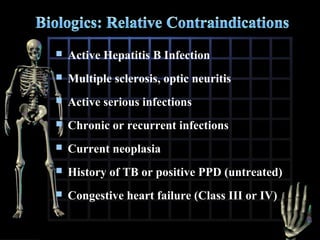
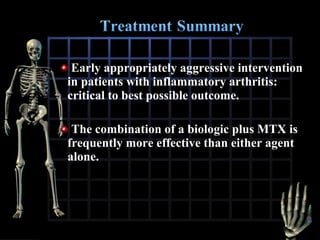
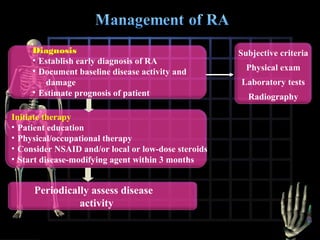
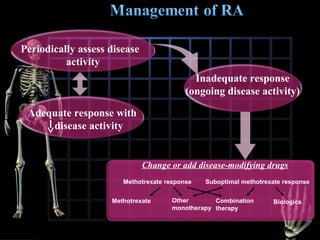
Rheumatoid arthritis is diagnosed based on a patient's history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests rather than a single test. Early diagnosis and treatment are important to slow disease progression and prevent structural joint damage. Treatment involves non-pharmacological measures as well as a variety of drug therapies including NSAIDs, DMARDs such as methotrexate, and biologic DMARDs, with the goal of relieving pain, reducing inflammation, and maintaining function. Ongoing monitoring of disease activity is needed to assess treatment effectiveness.