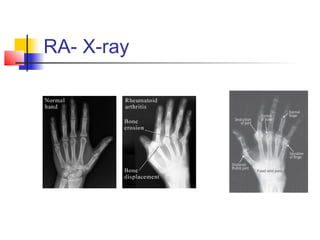
This document discusses rheumatoid arthritis, a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by symmetrical polyarthritis of small joints like those in the hands and feet. Key points include that it commonly affects middle-aged females and is associated with viruses. Symptoms include pain, swelling and morning stiffness of joints. Long-standing disease can cause joint deformities. Treatment involves disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs to prevent joint destruction and deformity, with methotrexate often used first line along with corticosteroids for symptom relief. Prognosis includes increased disability and reduced life expectancy by 5-10 years.